Should Renal Inflammation Be Targeted While Treating Hypertension?
- PMID: 35770194
- PMCID: PMC9236225
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.886779
Should Renal Inflammation Be Targeted While Treating Hypertension?
Abstract
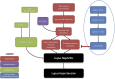
Despite extensive research and a plethora of therapeutic options, hypertension continues to be a global burden. Understanding of the pathological roles of known and underexplored cellular and molecular pathways in the development and maintenance of hypertension is critical to advance the field. Immune system overactivation and inflammation in the kidneys are proposed alternative mechanisms of hypertension, and resistant hypertension. Consideration of the pathophysiology of hypertension in chronic inflammatory conditions such as autoimmune diseases, in which patients present with autoimmune-mediated kidney inflammation as well as hypertension, may reveal possible contributors and novel therapeutic targets. In this review, we 1) summarize current therapies used to control blood pressure and their known effects on inflammation; 2) provide evidence on the need to target renal inflammation, specifically, and especially when first-line and combinatory treatment efforts fail; and 3) discuss the efficacy of therapies used to treat autoimmune diseases with a hypertension/renal component. We aim to elucidate the potential of targeting renal inflammation in certain subsets of patients resistant to current therapies.
Keywords: autoimmunity; blood pressure; immune cells; kidney; lupus; resistant hypertension; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2022 Chaudhari, Pham, Brooks, Dinh, Young-Stubbs, Shimoura and Mathis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aranow C., Atish-Fregoso Y., Lesser M., Mackay M., Anderson E., Chavan S., et al. (2021). Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Reduces Pain and Fatigue in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a Randomised, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Pilot Trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 80 (2), 203–208. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217872 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

