Relevance of Ferroptosis to Cardiotoxicity Caused by Anthracyclines: Mechanisms to Target Treatments
- PMID: 35770215
- PMCID: PMC9234116
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.896792
Relevance of Ferroptosis to Cardiotoxicity Caused by Anthracyclines: Mechanisms to Target Treatments
Abstract
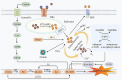
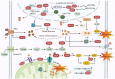
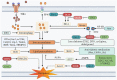
Anthracyclines (ANTs) are a class of anticancer drugs widely used in oncology. However, the clinical application of ANTs is limited by their cardiotoxicity. The mechanisms underlying ANTs-induced cardiotoxicity (AIC) are complicated and involve oxidative stress, inflammation, topoisomerase 2β inhibition, pyroptosis, immunometabolism, autophagy, apoptosis, ferroptosis, etc. Ferroptosis is a new form of regulated cell death (RCD) proposed in 2012, characterized by iron-dependent accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxidation. An increasing number of studies have found that ferroptosis plays a vital role in the development of AIC. Therefore, we aimed to elaborate on ferroptosis in AIC, especially by doxorubicin (DOX). We first summarize the mechanisms of ferroptosis in terms of oxidation and anti-oxidation systems. Then, we discuss the mechanisms related to ferroptosis caused by DOX, particularly from the perspective of iron metabolism of cardiomyocytes. We also present our research on the prevention and treatment of AIC based on ferroptosis. Finally, we enumerate our views on the development of drugs targeting ferroptosis in this emerging field.
Keywords: cardiotoxicity; doxorubicin; ferroptosis; iron; mechanism; treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Yuan, Su, Zhang, Gokulnath, Vulugundam, Li, Yang, An, Liu, Sun, Chen, Wu, Sun and Xing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: An overview from cellular structural perspective.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct;179:117312. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117312. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39167843 Review.
-
Cardiac Damage in Anthracyclines Therapy: Focus on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020 May 20;32(15):1081-1097. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8016. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020. PMID: 31928066 Review.
-
Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Feb 12;116(7):2672-2680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821022116. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30692261 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the role of ferroptosis in the doxorubicin-induced chronic cardiotoxicity using a murine model.Chem Biol Interact. 2022 Aug 25;363:110008. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110008. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Chem Biol Interact. 2022. PMID: 35667395
-
Doxorubicin causes ferroptosis and cardiotoxicity by intercalating into mitochondrial DNA and disrupting Alas1-dependent heme synthesis.Sci Signal. 2022 Nov;15(758):eabn8017. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abn8017. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Sci Signal. 2022. PMID: 36318618
Cited by
-
Natural Products for Preventing and Managing Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Comprehensive Review.Cells. 2024 Jul 6;13(13):1151. doi: 10.3390/cells13131151. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38995002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dual role of ferroptosis in anthracycline-based chemotherapy includes reducing resistance and increasing toxicity.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jun 21;9(1):184. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01483-1. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37344500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Ferroptosis in the Treatment of Mitochondrial Cardiomyopathies and Heart Failure.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 1;83(1):23-32. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001496. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37816193 Free PMC article.
-
The Application and Molecular Mechanisms of Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants in Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiac Injury.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Mar 7;47(3):176. doi: 10.3390/cimb47030176. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40136430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaced Anticancer Potential of Doxorubicin: Spotlight on Breast Cancer.Dis Res. 2025 Mar;5(1):19-36. doi: 10.54457/dr.202402015. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Dis Res. 2025. PMID: 40530298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zamorano JL, Lancellotti P, Rodriguez Muñoz D, Aboyans V, Asteggiano R, Galderisi M, et al. 2016 Esc position paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the esc committee for practice guidelines: the task force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the European society of cardiology (Esc). Eur Heart J. (2016) 37:2768–801. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw211 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

