PScL-DDCFPred: an ensemble deep learning-based approach for characterizing multiclass subcellular localization of human proteins from bioimage data
- PMID: 35771606
- PMCID: PMC9890309
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac432
PScL-DDCFPred: an ensemble deep learning-based approach for characterizing multiclass subcellular localization of human proteins from bioimage data
Abstract
Motivation: Characterization of protein subcellular localization has become an important and long-standing task in bioinformatics and computational biology, which provides valuable information for elucidating various cellular functions of proteins and guiding drug design.
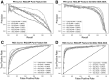
Results: Here, we develop a novel bioimage-based computational approach, termed PScL-DDCFPred, to accurately predict protein subcellular localizations in human tissues. PScL-DDCFPred first extracts multiview image features, including global and local features, as base or pure features; next, it applies a new integrative feature selection method based on stepwise discriminant analysis and generalized discriminant analysis to identify the optimal feature sets from the extracted pure features; Finally, a classifier based on deep neural network (DNN) and deep-cascade forest (DCF) is established. Stringent 10-fold cross-validation tests on the new protein subcellular localization training dataset, constructed from the human protein atlas databank, illustrates that PScL-DDCFPred achieves a better performance than several existing state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, the independent test set further illustrates the generalization capability and superiority of PScL-DDCFPred over existing predictors. In-depth analysis shows that the excellent performance of PScL-DDCFPred can be attributed to three critical factors, namely the effective combination of the DNN and DCF models, complementarity of global and local features, and use of the optimal feature sets selected by the integrative feature selection algorithm.
Availability and implementation: https://github.com/csbio-njust-edu/PScL-DDCFPred.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures





References
-
- Baudat G., Anouar F. (2000) Generalized discriminant analysis using a kernel approach. Neural Comput., 12, 2385–2404. - PubMed
-
- Boland M.V., Murphy R.F. (2001) A neural network classifier capable of recognizing the patterns of all major subcellular structures in fluorescence microscope images of HeLa cells. Bioinformatics, 17, 1213–1223. - PubMed
-
- Breiman L. (2001) Random forests. Mach. Learn., 45, 5–32.
-
- Chen T., Guestrin C. (2016) XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, California, USA. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, pp. 785–794.
-
- Chen C. et al. (2020) Improving protein–protein interactions prediction accuracy using XGBoost feature selection and stacked ensemble classifier. Comput. Biol. Med., 123, 103899. - PubMed

