Rural-Urban Differences in Diabetes Care and Control in 42 Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Cross-sectional Study of Nationally Representative Individual-Level Data
- PMID: 35771765
- PMCID: PMC9472489
- DOI: 10.2337/dc21-2342
Rural-Urban Differences in Diabetes Care and Control in 42 Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Cross-sectional Study of Nationally Representative Individual-Level Data
Abstract
Objective: Diabetes prevalence is increasing rapidly in rural areas of low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), but there are limited data on the performance of health systems in delivering equitable and effective care to rural populations. We therefore assessed rural-urban differences in diabetes care and control in LMICs.
Research design and methods: We pooled individual-level data from nationally representative health surveys in 42 countries. We used Poisson regression models to estimate age-adjusted differences in the proportion of individuals with diabetes in rural versus urban areas achieving performance measures for the diagnosis, treatment, and control of diabetes and associated cardiovascular risk factors. We examined differences across the pooled sample, by sex, and by country.
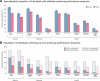
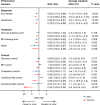
Results: The pooled sample from 42 countries included 840,110 individuals (35,404 with diabetes). Compared with urban populations with diabetes, rural populations had ∼15-30% lower relative risk of achieving performance measures for diabetes diagnosis and treatment. Rural populations with diagnosed diabetes had a 14% (95% CI 5-22%) lower relative risk of glycemic control, 6% (95% CI -5 to 16%) lower relative risk of blood pressure control, and 23% (95% CI 2-39%) lower relative risk of cholesterol control. Rural women with diabetes had lower achievement of performance measures relating to control than urban women, whereas among men, differences were small.
Conclusions: Rural populations with diabetes experience substantial inequities in the achievement of diabetes performance measures in LMICs. Programs and policies aiming to strengthen global diabetes care must consider the unique challenges experienced by rural populations.
© 2022 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. Brussels, International Diabetes Federation, 2021
-
- Zabetian A, Sanchez IM, Narayan KM, Hwang CK, Ali MK. Global rural diabetes prevalence: a systematic review and meta-analysis covering 1990-2012. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014;104:206–213 - PubMed
-
- Strasser R, Kam SM, Regalado SM. Rural health care access and policy in developing countries. Annu Rev Public Health 2016;37:395–412 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

