A circular mRNA vaccine prototype producing VFLIP-X spike confers a broad neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by mouse sera
- PMID: 35772601
- PMCID: PMC9235288
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105370
A circular mRNA vaccine prototype producing VFLIP-X spike confers a broad neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by mouse sera
Abstract
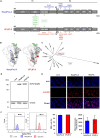
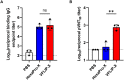
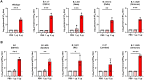
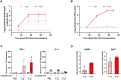
Next-generation COVID-19 vaccines are critical due to the ongoing evolution of SARS-CoV-2 virus and rapid waning duration of the neutralizing antibody response against current vaccines. The mRNA vaccines mRNA-1273 and BNT162b2 were developed using linear transcripts encoding the prefusion-stabilized trimers (S-2P) of the wildtype spike, which have shown a reduced neutralizing activity against the variants of concern B.1.617.2 and B.1.1.529. Recently, a new version of spike trimer, termed VFLIP (five (V) prolines, Flexibly-Linked, Inter-Protomer disulfide) was developed. Based on the original amino acid sequence of the wildtype spike, VFLIP was genetically engineered by using five proline substitutions, a flexible cleavage site amino acid linker, and an inter-protomer disulfide bond. It has been suggested to possess native-like glycosylation, and greater pre-fusion trimeric stability as opposed to S-2P. Here, we report that the spike protein VFLIP-X, containing six rationally substituted amino acids to reflect emerging variants (K417N, L452R, T478K, E484K, N501Y and D614G), offers a promising candidate for a next-generation SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Mice immunized by a circular mRNA (circRNA) vaccine prototype producing VFLIP-X had detectable neutralizing antibody titers for up to 7 weeks post-boost against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) and variants of interest (VOIs). In addition, a balance in TH1 and TH2 responses was achieved by immunization with VFLIP-X. Our results indicate that the VFLIP-X delivered by circRNA induces humoral and cellular immune responses, as well as broad neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; Spike; VFLIP; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

