Glyphosate-induced liver and kidney dysfunction, oxidative stress, immunosuppression in Nile tilapia, but ginger showed a protection role
- PMID: 35773603
- PMCID: PMC10209248
- DOI: 10.1007/s11259-022-09961-0
Glyphosate-induced liver and kidney dysfunction, oxidative stress, immunosuppression in Nile tilapia, but ginger showed a protection role
Abstract
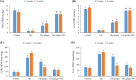
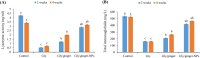
The water-borne herbicides are involved in the toxicity of aquatic animals resulting in impaired health status and low productivity. Dietary medicinal herbs present a practical solution to relieve the impacts of herbicides toxicity on the performances of aquatic animals. Herein, we investigated the toxicity of commercial glyphosate-induced oxidative stress, immunosuppression, liver and kidney dysfunction, and the protective role of ginger or ginger nanoparticles in Nile tilapia. Fish were allocated into four groups: the first group presented the control without glyphosate toxicity and ginger feeding, the second group intoxicated with glyphosate at 0.6 mg/L and fed ginger free diet, the third group intoxicated with glyphosate and fed ginger at 2.5 g/kg, and the fourth group intoxicated with glyphosate and fed ginger nanoparticles at 2.5 g/kg. Fish were kept under the experimental conditions for four weeks, and the samples of blood and tissues were collected after 2 and 4 weeks. Markedly, fish exposed to glyphosate showed the highest ALT and AST activities, glucose and cortisol levels, and malondialdehyde levels (MDA) in gills and tissues. While fish in the control and fish intoxicated with glyphosate and fed ginger nanoparticles had the lowest ALT and AST activities, glucose and cortisol levels, and MDA levels after 2 and 4 weeks (P < 0.05). Fish fed dietary ginger had lower ALT and AST activities, glucose and cortisol levels, and MDA levels than the glyphosate intoxicated group after 2 and 4 weeks (P < 0.05). Interestingly, fish-fed ginger nanoparticles showed lower urea and creatinine levels and higher total protein, albumin, and globulin than the glyphosate intoxicated group (P < 0.05) and similar to the control (P > 0.05). Further, fish intoxicated with glyphosate and fed ginger nanoparticles had the highest GSH, lysozyme activity, and immunoglobulin levels after 2 and 4 weeks (P < 0.05). In conclusion, ginger nanoparticles are superior to the standard ginger form in enhancing the antioxidative and immune responses of Nile tilapia exposed to glyphosate.
Keywords: Aquaculture nutrition; Blood metabolites; Herbicides; Immunity; Medicinal herbs; Oxidative stress.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
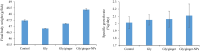
References
-
- Abdelmagid AD, El Asely AM, Said AM. Evaluation of Foeniculum vulgare impact on glyphosate hepato-toxicity in Nile tilapia: biochemical, molecular and histopathological study. Aquac Res. 2021;52:5397–5406. doi: 10.1111/are.15409. - DOI
-
- Acar Ü, İnanan BE, Navruz FZ, Yılmaz S. Alterations in blood parameters, DNA damage, oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes and immune-related genes expression in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to glyphosate-based herbicide. Comp Biochem Physiol c Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021;249:109147. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.109147. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Ghanim KA, Mahboob S, Vijayaraghavan P, Al-Misned FA, Kim YO, Kim H-J. Sub-lethal effect of synthetic pyrethroid pesticide on metabolic enzymes and protein profile of non-target Zebrafish, Danio rerio. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. 2020;27:441–447. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.11.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

