Evaluating future risk of NAFLD in adolescents: a prediction and decision curve analysis
- PMID: 35773644
- PMCID: PMC9245230
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-022-02401-y
Evaluating future risk of NAFLD in adolescents: a prediction and decision curve analysis
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the commonest liver condition in the western world and is directly linked to obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Elevated body mass index is regarded as a major risk factor of NAFL (steatosis) and NAFLD fibrosis. Using data from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC), we sought to investigate whether other variables from adolescence could improve prediction of future NAFL and NAFLD fibrosis risk at 24 years, above BMI and sex.
Methods: Aged 24 years, 4018 ALSPAC participants had transient elastography (TE) and controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) measurement using Echosens 502 Touch. 513 participants with harmful alcohol consumption were excluded. Logistic regression models examined which variables measured at 17 years were predictive of NAFL and NAFLD fibrosis in young adults. Predictors included sex, BMI, central adiposity, lipid profile, blood pressure, liver function tests, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and ultrasound defined NAFL at 17 years (when examining fibrosis outcomes). A model including all these variables was termed "routine clinical measures". Models were compared using area under the receiver operator curve (AUROC) and Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), analysis, which penalises model complexity. Models were tested in all participants and those with overweight or obese standardised BMIs (BMI SDS) centiles at the 17-year time point. A decision curve analysis (DCA) was performed to evaluate the clinical utility of models in overweight and obese adolescents predicting NAFLD fibrosis at a threshold probability of 0.1.
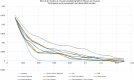
Results: The "routine clinical measures" model had the highest AUROC for predicting NAFL in all adolescent participants (AUROC 0.79 [SD 0.00]) and those with an overweight/obese BMI SDS centile (AUROC 0.77 [SD 0.01]). According to BIC analysis, insulin resistance was the best predictor of NAFL in all adolescents, whilst central adiposity was the best predictor in those with an overweight/obese BMI SDS centile. The "routine clinical measures" model also had the highest AUROC for predicting NAFLD fibrosis in all adolescent participants (AUROC 0.78 [SD 0.02]) and participants with an overweight/obese BMI SDS centile (AUROC 0.84 [SD 0.03]). However, following BIC analysis, BMI was the best predictor of NAFLD fibrosis in all adolescents including those with an overweight/obese BMI SDS centile. A decision curve analysis examining overweight/obese adolescent participants showed the model that had the greatest net benefit for increased NAFLD fibrosis detection, above a treat all overweight and obese adolescents' assumption, was the "routine clinical measures" model. However, the net benefit was marginal (0.0054 [0.0034-0.0075]).
Conclusion: In adolescents, routine clinical measures were not superior to central adiposity and BMI at predicting NAFL and NAFLD fibrosis respectively in young adulthood. Additional routine clinical measurements do provide incremental benefit in detecting true positive fibrosis cases, but the benefit is small. Thus, to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with NASH cirrhosis in adults, the ultimate end point of NAFLD, the focus must be on obesity management at a population level.
Keywords: ALSPAC (Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children); Body composition; NAFLD (nonalcoholc fatty liver disease); Obesity; Young adults.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of steatosis and fibrosis in young adults in the UK: a population-based study.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar;5(3):295-305. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30419-4. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31954687 Free PMC article.
-
Association of whole blood copper, zinc, calcium, magnesium, and iron with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in overweight and obese children.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Mar 28;49(3):426-434. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.230274. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38970517 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is an independent predictor of liver fibrosis among pediatrics non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 16;13:1071350. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1071350. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36589844 Free PMC article.
-
Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the overweight and obese population: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Jan;8(1):20-30. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00317-X. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36400097
-
[A cross-sectional study on the prevalence rate and influencing factors of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in overweight/obese children].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023 May 15;25(5):448-456. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2211018. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37272169 Free PMC article. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Machine learning survival models for Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on a health checkup cohort.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 15;25(1):518. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04120-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40660095 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic machine learning model for prediction of NAFLD in a health checkup population: A longitudinal study.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 27;9(8):e18758. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18758. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37576311 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram model for predicting the risk of MAFLD in the young population.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 23;14(1):9376. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60100-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38654043 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Ultrasound for the Detection of Possible Fatty Liver Disease in Children.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jul 31;14(15):1652. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14151652. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39125528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pembroke T, John G, Michalak O, Puyk B, Salmon J, Godkin A, et al. The progression of liver disease in 69,290 individuals in Wales from 1999–2019: tracking the evolution of liver disease. J Hepatol. 2020;73:S46. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(20)30641-3. - DOI
-
- Flemming J, Djerboua M, Booth C, Terrault N. Increasing burden of cirrhosis projected to 2040 in Canada: implications for prevention, screening, and management. J Hepatol. 2020;73:S45. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(20)30640-1. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous