Antimicrobial stewardship using electronic prescribing systems in hospital settings: a scoping review of interventions and outcome measures
- PMID: 35774070
- PMCID: PMC9237448
- DOI: 10.1093/jacamr/dlac063
Antimicrobial stewardship using electronic prescribing systems in hospital settings: a scoping review of interventions and outcome measures
Abstract
Objectives: To identify interventions implemented in hospital electronic prescribing systems and the outcome measures used to monitor their impact.
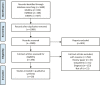
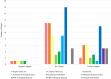
Methods: We systematically searched CINAHL, EMBASE, Google Scholar and Medline using keywords in three strands: (i) population: hospital inpatient or emergency department; (ii) intervention: electronic prescribing functionality; and (iii) outcome: antimicrobial stewardship. The interventions were grouped into six themes: alerts, order sets, restriction of access, mandated documentation, embedded guidelines and automatic prescription stop. The outcome measures were organized into those that measure the quality or quantity of prescribing or clinical decision support (CDS) activity. The impact of each intervention reported was grouped into a positive, negative or no change.
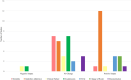
Results: A total of 28 studies were eligible for inclusion. There were 28 different interventions grouped into the six themes. Alerts visible to the practitioner in the electronic health record (EHR) were most frequently implemented (n = 11/28). Twenty different outcome measures were identified, divided into quality (n = 13/20) and quantity outcomes (n = 4/20) and CDS activity (n = 3/20). One-third of outcomes reported across the 28 studies showed positive change (34.4%, n = 42/122) and 61.4% (n = 75/122) showed no change.
Conclusions: The most frequently implemented interventions were alerts, the majority of which were to influence behaviour or decision-making of the practitioner within the EHR. Quality outcomes were most frequently selected by researchers. The review supports previous research that larger well-designed randomized studies are needed to investigate the impact of interventions on AMS and outcome measures to be standardized.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2015. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/193736/9789241509763_en....
-
- NICE . Antimicrobial Stewardship: Systems and Processes ford Effective Antimicrobial Medicine Use—NICE Guideline [NG15]. 2015. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng15.
-
- Cresswell K, Mozaffar H, Shah Set al. . Approaches to promoting the appropriate use of antibiotics through hospital electronic prescribing systems: a scoping review. Int J Pharm Pract 2017; 25: 5–17. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources