Cinnamaldehyde Mitigates Atherosclerosis Induced by High-Fat Diet via Modulation of Hyperlipidemia, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation
- PMID: 35774377
- PMCID: PMC9239836
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4464180
Cinnamaldehyde Mitigates Atherosclerosis Induced by High-Fat Diet via Modulation of Hyperlipidemia, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation
Abstract
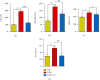
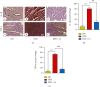
Atherosclerosis is a disease in which plaque builds up inside arteries. Cinnamaldehyde (Ci) has many biological properties that include anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. Thus, this study was designed to explore the protective effect of Ci against atherosclerosis induced by a high-fat diet (HFD) in Wistar rats. Atherosclerosis was induced by an oral administration of an HFD for 10 weeks. Atherosclerosis-induced rats were supplemented with Ci at a dose of 20 mg/kg bw dissolved in 0.5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), daily by oral gavage for the same period. Rats were divided into three groups of 10 rats each fed with (a) ND, (b) HFD, and (c) HFD+Ci, daily for 10 weeks. Treatment of rats with Ci significantly reduced the elevated levels of serum total cholesterol (T.Ch), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-Ch), very low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (VLDL-Ch), and free fatty acids (FFAs) and significantly increased the lowered levels of high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-Ch) level. Ci ameliorated the increased cardiovascular risk indices 1 and 2 and the decreased antiatherogenic index. Moreover, Ci reduced the elevated serum creatine kinase (CK), creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activities. Ci also improved the heart antioxidant activities by decreasing malondialdehyde (MDA) and increasing glutathione S-transferase (GST), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), reduced glutathione (GSH), and glutathione peroxidase (Gpx) activities. Furthermore, the supplementation with Ci downregulated the mRNA expression levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-17 (IL-17), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Thus, Ci successfully elicited a therapeutic impact against atherosclerosis induced by HFD via its hypolipidemic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory actions.
Copyright © 2022 Basma S. Ismail et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Anti-atherosclerosis of oligomeric proanthocyanidins from Rhodiola rosea on rat model via hypolipemic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities together with regulation of endothelial function.Phytomedicine. 2018 Dec 1;51:171-180. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30466614
-
Esculeogenin A, a Glycan from Tomato, Alleviates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Rats through Hypolipidemic, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Effects.Nutrients. 2023 Nov 11;15(22):4755. doi: 10.3390/nu15224755. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38004149 Free PMC article.
-
Lycopene corrects metabolic syndrome and liver injury induced by high fat diet in obese rats through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Sep;141:111831. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111831. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34237596
-
Icariin Attenuates High-cholesterol Diet Induced Atherosclerosis in Rats by Inhibition of Inflammatory Response and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2016 Feb;39(1):228-236. doi: 10.1007/s10753-015-0242-x. Inflammation. 2016. PMID: 26307750
-
Protective effect of hydroxychloroquine on rheumatoid arthritis-associated atherosclerosis.Animal Model Exp Med. 2019 Apr 19;2(2):98-106. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12065. eCollection 2019 Jun. Animal Model Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31392302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of cinnamon supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in adults: a GRADE assessed systematic review, dose-response and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Health Popul Nutr. 2025 Jul 3;44(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s41043-025-00967-3. J Health Popul Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40611215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histological, ultrastructural and immunohistochemical studies on the ameliorative role of Cinnamon zeylanicum against high cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in the kidney of adult male albino rats.Heliyon. 2022 Aug 24;8(8):e10401. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10401. eCollection 2022 Aug. Heliyon. 2022. Retraction in: Heliyon. 2023 Jul 05;9(7):e17932. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17932. PMID: 36090212 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Green Tea Pressurized Hot Water Extract in Atherosclerosis: A Multi-Approach Study on Cellular, Animal, and Molecular Mechanisms.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 28;14(4):404. doi: 10.3390/antiox14040404. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298660 Free PMC article.
-
Influence and molecular mechanism of cinnamaldehyde against ventricular arrhythmia via the TAK1-p38MAPK-NLRP3 pathway.Heart Vessels. 2025 Sep;40(9):846-861. doi: 10.1007/s00380-025-02529-3. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Heart Vessels. 2025. PMID: 40146271 Free PMC article.
-
The role and mechanism of cinnamaldehyde in cancer.J Food Drug Anal. 2024 Jun 15;32(2):140-154. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.3502. J Food Drug Anal. 2024. PMID: 38934689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu C. H., Yang M. Y., Chan K. C., Chung P. J., Ou T. T., Wang C. J. Improvement in high-fat diet-induced obesity and body fat accumulation by a Nelumbo nucifera leaf flavonoid-rich extract in mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry . 2010;58(11):7075–7081. doi: 10.1021/jf101415v. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

