Modularisation of published and novel models toward a complex KIR2DL4 pathway in pbNK cell
- PMID: 35774414
- PMCID: PMC9237949
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2022.101760
Modularisation of published and novel models toward a complex KIR2DL4 pathway in pbNK cell
Abstract
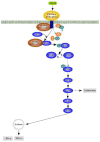
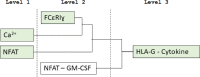
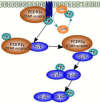
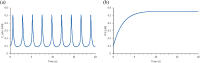
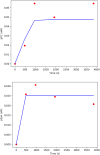
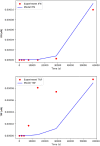
KIR2DL4 is an interesting receptor expressed on the peripheral blood natural killer (pbNK) cell as it can be either activating or inhibitory depending on the amino acid residues in the domain. This model uses mathematical modelling to investigate the downstream effects of natural killer cells' activation (KIR2DL4) receptor after stimulation by key ligand (HLA-G) on pbNK cells. Development of this large pathway is based on a comprehensive qualitative description of pbNKs' intracellular signalling pathways leading to chemokine and cytotoxin secretion, obtained from the KEGG database (https://www.genome.jp/pathway/hsa04650). From this qualitative description we built a quantitative model for the pathway, reusing existing curated models where possible and implementing new models as needed. This model employs a composite approach for generating modular models. The approach allows for the construction of large-scale complex model by combining component of sub-models that can be modified individually. This large pathway consists of two published sub-models; the Ca2+ model and the NFAT model, and a newly built FCεRIγ sub-model. The full pathway was fitted to published dataset and fitted well to one of two secreted cytokines. The model can be used to predict the production of IFNγ and TNFα cytokines.•Development of pathway and mathematical model•Reusing existing curated models and implementing new models•Model optimization and analysis.
Keywords: Intracellular signalling pathway; Mathematical model; Modularisation.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
KIR2DL4 (CD158d): An activation receptor for HLA-G.Front Immunol. 2012 Aug 20;3:258. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00258. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22934097 Free PMC article.
-
Differential microRNA expression between decidual and peripheral blood natural killer cells in early pregnancy.Hum Reprod. 2018 Dec 1;33(12):2184-2195. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dey323. Hum Reprod. 2018. PMID: 30388265
-
Endosomal signaling and a novel pathway defined by the natural killer receptor KIR2DL4 (CD158d).Traffic. 2010 Nov;11(11):1381-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01112.x. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20854369 Review.
-
The genotype of the NK cell receptor, KIR2DL4, influences INFgamma secretion by decidual natural killer cells.Mol Hum Reprod. 2009 Aug;15(8):489-97. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gap039. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Mol Hum Reprod. 2009. PMID: 19509110
-
Roles of HLA-G/KIR2DL4 in Breast Cancer Immune Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 3;13:791975. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.791975. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35185887 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sica A., Dorman L., Viggiano V., Cippitelli M., Ghosh P., Rice N., Young H.A. Interaction of nf-κb and nfat with the interferon-γ promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272(48):30412–30420. - PubMed
-
- Pfeiffer J.R., Oliver J.M. Tyrosine kinase-dependent assembly of actin plaques linking fc epsilon R1 cross-linking to increased cell substrate adhesion in RBL-2H3 tumor mast cells. J. Immunol. 1994;152(1):270–279. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

