Automation of Cephalometrics Using Machine Learning Methods
- PMID: 35774443
- PMCID: PMC9239774
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3061154
Automation of Cephalometrics Using Machine Learning Methods
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Automation of Cephalometrics Using Machine Learning Methods.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9831054. doi: 10.1155/2023/9831054. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38124813 Free PMC article.
Abstract
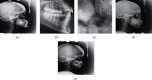
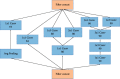
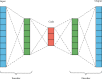
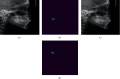
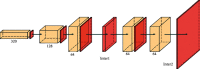
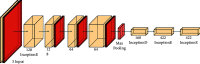
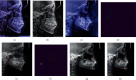
Cephalometry is a medical test that can detect teeth, skeleton, or appearance problems. In this scenario, the patient's lateral radiograph of the face was utilised to construct a tracing from the tracing of lines on the lateral radiograph of the face of the soft and hard structures (skin and bone, respectively). Certain cephalometric locations and characteristic lines and angles are indicated after the tracing is completed to do the real examination. In this unique study, it is proposed that machine learning models be employed to create cephalometry. These models can recognise cephalometric locations in X-ray images, allowing the study's computing procedure to be completed faster. To correlate a probability map with an input image, they combine an Autoencoder architecture with convolutional neural networks and Inception layers. These innovative architectures were demonstrated. When many models were compared, it was observed that they all performed admirably in this task.
Copyright © 2022 Khalaf Alshamrani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Kannan S. K. A simplified overview on clinical cephalometrics PJ Antony, S.karthiga Kanannan, Joby paulose, Manu M Mathew, Charis chandy joseph. Journal of Indian Academy of Oral Medicine and Radiology . 2013;25(3):214–217.
-
- Agrawal D. Cephalometric analysis for Diagnosis and treatment of orthodontic patients. Journal of Oral Health and Community Dentistry . 2013;7(2):75–79. doi: 10.5005/johcd-7-2-75. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

