Brainstem Toxicity in Pediatric Patients Treated with Protons Using a Single-vault Synchrocyclotron System
- PMID: 35774490
- PMCID: PMC9238130
- DOI: 10.14338/IJPT-22-00008.1
Brainstem Toxicity in Pediatric Patients Treated with Protons Using a Single-vault Synchrocyclotron System
Abstract
Purpose: Cranial radiation therapy remains an integral component of curative treatment for pediatric patients with brain tumors. Proton beam radiation therapy (PBT) can limit collateral radiation dose to surrounding normal tissue, thus reducing off-target exposure while maintaining appropriate tumor coverage. While PBT offers significant advantages over photon therapy for pediatric patients with intracranial malignancies, cases of brainstem necrosis after PBT have raised concerns that PBT may pose an increased risk of necrosis over photon therapy. We investigated the incidence of brainstem necrosis at our institution in children treated with PBT for intracranial malignancies.
Patients and methods: Patients with pediatric brain tumor treated with passively scattered PBT, using a gantry-mounted, synchrocyclotron single-vault system between 2013 and 2018, were retrospectively reviewed. Inclusion criteria included patients 21 years of age or younger who received a minimum 0.1 cm3 maximum brainstem dose of 50 Gray relative biological effectiveness (GyRBE). Patients were assessed for "central nervous system necrosis" in the brainstem per the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 5.0 (US National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Maryland) criteria.
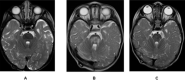
Results: Fifty-eight patients were included for analysis. The median age was 10.3 years. Twenty-one (36.2%) patients received craniospinal irradiation. Thirty-four (58.6%) patients received chemotherapy. The median prescription radiation dose was 54 GyRBE. Regarding published dosimetric constraints used at 3 separate proton centers, the goal brainstem D50% <52 GyRBE was exceeded in 23 (40%) patients, but the brainstem Dmax <58 GyRBE was not exceeded in any patients. No patient experienced grade ≥2 brainstem injury. One patient demonstrated radiographic changes consistent with grade 1 toxicity. This patient had myeloablative chemotherapy with tandem stem cell rescue before PBT.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrates a low risk of any brainstem injury in children treated with passively scattered PBT using a single-vault synchrocyclotron.
Keywords: brainstem; passive-scatter; pediatrics; radionecrosis; synchrocyclotron.
©Copyright 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Duffner PK. Risk factors for cognitive decline in children treated for brain tumors. Eur J Paediatr Neurol . 2010;14:106–15. - PubMed
-
- Hall MD, Bradley JA, Rotondo RL, Hanel R, Shah C, Morris CG, Aldana PR, Indelicato DJ. Risk of radiation vasculopathy and stroke in pediatric patients treated with proton therapy for brain and skull base tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys . 2018;101:854–9. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong GT, Liu Q, Yasui Y, Huang S, Ness KK, Leisenring W, Hudson MM, Donaldson SS, King AA, Stovall M, Krull KR, Robison LL, Packer RJ. Long-term outcomes among adult survivors of childhood central nervous system malignancies in the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J Natl Cancer Inst . 2009;101:946–58. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
