Dosimetric Comparison of Various Spot Placement Techniques in Proton Pencil Beam Scanning
- PMID: 35774494
- PMCID: PMC9238129
- DOI: 10.14338/IJPT-21-00022.1
Dosimetric Comparison of Various Spot Placement Techniques in Proton Pencil Beam Scanning
Abstract
Purpose: To present quantitative dosimetric evaluations of five proton pencil beam spot placement techniques.
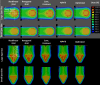
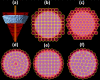
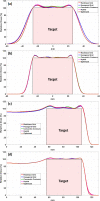
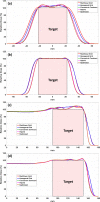
Materials and methods: The spot placement techniques that were investigated include two grid-based (rectilinear grid and hexagonal grid, both commonly available in commercial planning systems) and three boundary-contoured (concentric contours, hybrid, and optimized) techniques. Treatment plans were created for two different target volumes, one spherical and one conical. An optimal set of planning parameters was defined for all treatment plans and the impact of spot placement techniques on the plan quality was evaluated in terms of lateral/distal dose falloff, normal tissue sparing, conformity and homogeneity of dose distributions, as well as total number of spots used.
Results: The results of this work highlight that for grid-based spot placement techniques, the dose conformity is dependent on target cross-sectional shape perpendicular to beam direction, which changes for each energy layer. This variable conformity problem is mitigated by using boundary contoured spot placement techniques. However, in the case of concentric contours, the conformity is improved but at the cost of decreased homogeneity inside the target. Hybrid and optimized spot placement techniques, which use contoured spots at the boundary and gridlike interior spot patterns, provide more uniform dose distributions inside the target volume while maintaining the improved dose conformity. The optimized spot placement technique improved target coverage, homogeneity of dose, and minimal number of spots. The dependence of these results on spot size is also presented for both target shapes.
Conclusion: This work illustrates that boundary-contoured spot placement techniques offer marked improvement in dosimetry metrics when compared to commercially available grid-based techniques for a range of proton scanned beam spot sizes.
Keywords: proton therapy; spot placement in proton pencil beam scanning.
©Copyright 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Kevin Erhart, PhD, is an employee of .decimal LLC, a manufacturer of proton treatment planning software and custom treatment devices. The other authors have no additional conflicts to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Pedroni E, Bacher R, Blattmann H, Böhringer T, Coray A, Lomax A, Lin S, Munkel G, Scheib S, Schneider U. The 200-MeV proton therapy project at the Paul Scherrer Institute: conceptual design and practical realization. Med Phys . 1995;22:37–53. - PubMed
-
- Alshaikhi J, Doolan PJ, D'Souza D, Holloway SM, Amos RA, Royle G. Impact of varying planning parameters on proton pencil beam scanning dose distributions in four commercial treatment planning systems. Med Phys . 2019;46:1150–62. - PubMed
-
- Kraan AC, Depauw N, Clasie B, Giunta M, Madden T, Kooy HM. Effects of spot parameters in pencil beam scanning treatment planning. Med Phys . 2018;45:60–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
