Pneumonia Caused by Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Positive for Exfoliative Toxin A and Secondary to Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
- PMID: 35774683
- PMCID: PMC9236638
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.25334
Pneumonia Caused by Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Positive for Exfoliative Toxin A and Secondary to Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
Abstract
Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) causes severe pneumonia. Previous reports found that CA-MRSA producing the Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) or toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) triggered severe necrotizing pneumonia. However, other toxins and genetic factors responsible for CA-MRSA pneumonia are rarely analyzed in Japan. In this study, we performed whole-genome sequencing (WGS) to analyze the clinical features of CA-MRSA genetically. As a result, we identified a strain with a rare sequence-type of MRSA. Herein, we present a case of CA-MRSA pneumonia in a 64-year-old woman. Her condition improved rapidly with vancomycin therapy. Draft WGS led to identifying the genotype and virulence factors and showed that the strain was a rare sequence-type of MRSA with the following characteristics: staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) type IV, sequence type 121, exfoliative toxin A-positive, and specific staphylococcal protein A type t5110. To the best of our knowledge, a strain with this profile has not been previously reported. Our findings provide new insights into CA-MRSA pneumonia and its genetic and clinical features. Therefore, we recommend accumulating genetic profiles of CA-MRSA pneumonia to identify genetic features and the clinical characteristics of the patients.
Keywords: community-acquired methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus; community-acquired pneumonia; exfoliative toxin a; sequence type 121; whole-genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2022, Itano et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
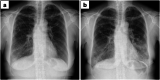
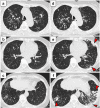
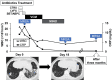
References
-
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lee AS, de Lencastre H, Garau J, Kluytmans J, Malhotra-Kumar S, Peschel A, Harbarth S. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18033. - PubMed
-
- Comparison of community- and health care-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Naimi TS, LeDell KH, Como-Sabetti K, et al. JAMA. 2003;290:2976–2984. - PubMed
-
- Molecular characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains isolated from patients with bacteremia based on MLST, SCCmec, spa, and agr locus types analysis. Goudarzi M, Seyedjavadi SS, Nasiri MJ, Goudarzi H, Sajadi Nia R, Dabiri H. Microb Pathog. 2017;104:328–335. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
