The Effectiveness and Safety of Ropivacaine and Medium-Dose Dexmedetomidine in Cesarean Section
- PMID: 35774754
- PMCID: PMC9239787
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4447484
The Effectiveness and Safety of Ropivacaine and Medium-Dose Dexmedetomidine in Cesarean Section
Retraction in
-
Retracted: The Effectiveness and Safety of Ropivacaine and Medium-Dose Dexmedetomidine in Cesarean Section.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9823465. doi: 10.1155/2023/9823465. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37387892 Free PMC article.
Abstract
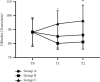
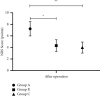
Objective: To study the effects of epidural anesthesia with different doses of dexmedetomidine and ropivacaine on postoperative hemodynamics and neonatal outcome of cesarean section parturients. Methods. A total of 90 parturients who underwent cesarean section admitted to our hospital from January 2019 to January 2020 were selected as the research objects and were divided into groups A, B, and C according to different dosages of dexmedetomidine, with 30 cases in each group. Groups A, B, and C were given dexmedetomidine 0.5 μg/kg, 0.8 μg/kg, 1.0 μg/kg, respectively, combined with 0.2% ropivacaine. The anesthesia effect, traction response, hemodynamic indexes, and neonatal Apgar score of the three groups were compared; the "Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) Score" was used to assess the postoperative pain of the parturients, and the "Ramsay Sedation Scale" was used to assess the sedation state of the parturients. Results. The superior anesthesia effect of group B was obtained compared with groups A and C (P < 0.05). Group B witnessed a lower degree of grade III stretching response, as compared to group A (P < 0.05). In comparison with groups A and C, superior results of the heart rate and mean artery pressure (MAP) of group B at T1 and T2 were obtained (P < 0.05). The neonatal Apgar score in group B was lower than those in groups A and C (P < 0.05), and the NRS score of group B was also lower than that of group A (P < 0.05). Compared with groups A and C, group B yielded a more favorable outcome in terms of the Ramsay score (P < 0.05). Conclusion. The use of medium-dose dexmedetomidine in cesarean section parturients is safer and can effectively reduce the impact on maternal hemodynamics, which is worthy of promotion and application.
Copyright © 2022 Bin-Bin Huang and Shi-Kun Niu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Liu X., Zhang X., Wang X., Wang J., Wang H. Comparative evaluation of intrathecal bupivacaine alone and bupivacaine combined with dexmedetomidine in cesarean section using spinal anesthesia: a meta-analysis. Journal of International Medical Research . 2019;47(7):2785–2799. doi: 10.1177/0300060518797000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hayley A. C., Green M., Downey L. A., et al. Neurocognitive performance under combined regimens of ketamine-dexmedetomidine and ketamine-fentanyl in healthy adults: a randomised trial. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry: An International Research, Review and News Journal . 2019;94109647 - PubMed
-
- Hatami M., Mashayekhi M., Abbasi H., Ayatollahi V., Vaziribozorg S. Comparing the effect of dexmedetomidine and labetalol on hemodynamic variables in patients undergoing microlaryngoscopy. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology . 2019;276(9):2513–2517. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05521-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xing N., Xing F., Li Y., et al. Dexmedetomidine improves propofol-induced neuronal injury in rat hippocampus with the involvement of miR-34a and the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Life Sciences . 2020;247 - PubMed
-
- Li Y., Jiang X., Wang J., et al. Intravenous dexmedetomidine combined with ultrasound-guided rectus sheath block for open gastrectomy: a prospective randomized trial. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery: Official Journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract . 2020;24(6):1290–1297. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

