Immunomodulatory role of T helper cells in rheumatoid arthritis : a comprehensive research review
- PMID: 35775145
- PMCID: PMC9350707
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.117.BJR-2021-0594.R1
Immunomodulatory role of T helper cells in rheumatoid arthritis : a comprehensive research review
Abstract
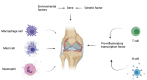
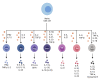
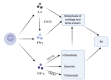
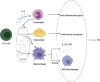
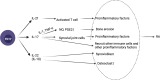
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that involves T and B cells and their reciprocal immune interactions with proinflammatory cytokines. T cells, an essential part of the immune system, play an important role in RA. T helper 1 (Th1) cells induce interferon-γ (IFN-γ), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin (IL)-2, which are proinflammatory cytokines, leading to cartilage destruction and bone erosion. Th2 cells primarily secrete IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, which exert anti-inflammatory and anti-osteoclastogenic effects in inflammatory arthritis models. IL-22 secreted by Th17 cells promotes the proliferation of synovial fibroblasts through induction of the chemokine C-C chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2). T follicular helper (Tfh) cells produce IL-21, which is key for B cell stimulation by the C-X-C chemokine receptor 5 (CXCR5) and coexpression with programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and/or inducible T cell costimulator (ICOS). PD-1 inhibits T cell proliferation and cytokine production. In addition, there are many immunomodulatory agents that promote or inhibit the immunomodulatory role of T helper cells in RA to alleviate disease progression. These findings help to elucidate the aetiology and treatment of RA and point us toward the next steps. Cite this article: Bone Joint Res 2022;11(7):426-438.
Keywords: Immunomodulatory; Interleukin; Rheumatoid arthritis; T helper cells; aetiology; autoimmune diseases; cartilage destruction; chemokines; cytokines; fibroblasts; inflammatory arthritis; tumour necrosis factor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Detection of peripheral follicular helper T cells in rheumatoid arthritis].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Dec 18;48(6):951-957. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 27987496 Chinese.
-
Protection against cartilage and bone destruction by systemic interleukin-4 treatment in established murine type II collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):81-91. doi: 10.1186/ar14. Epub 1999 Oct 26. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056663 Free PMC article.
-
T helper cells in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis primarily have a Th1 and a CXCR3+Th2 phenotype.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Oct 16;22(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02349-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33066816 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand (CXCL)10 in autoimmune diseases.Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Mar;13(3):272-80. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.10.010. Epub 2013 Nov 2. Autoimmun Rev. 2014. PMID: 24189283 Review.
-
[T follicular helper cells and their related molecules in rheumatoid arthritis: A review].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Mar;35(3):281-286. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31030723 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Advanced immunophenotyping: A powerful tool for immune profiling, drug screening, and a personalized treatment approach.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 24;14:1096096. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1096096. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37033944 Free PMC article.
-
Contemporary outcomes of primary total hip arthroplasty in patients with inflammatory arthritis.Bone Joint J. 2023 Jul 1;105-B(7):768-774. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.105B7.BJJ-2023-0220.R1. Bone Joint J. 2023. PMID: 37399088 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Immunotherapy for SMARCA4-Deficient Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma (SDUS).Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 11;14(8):987. doi: 10.3390/biom14080987. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199375 Free PMC article.
-
Helper T Cells are Hyperactive and Contribute to the Dysregulation of Antibody Production in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 23;25(18):10190. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810190. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337675 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterials for Modulating the Immune Microenvironment in Rheumatoid Arthritis.BME Front. 2025 Mar 10;6:0102. doi: 10.34133/bmef.0102. eCollection 2025. BME Front. 2025. PMID: 40065832 Free PMC article. Review.

