Efficacy of rifaximin against covert hepatic encephalopathy and hyperammonemia in Japanese patients
- PMID: 35776720
- PMCID: PMC9249214
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270786
Efficacy of rifaximin against covert hepatic encephalopathy and hyperammonemia in Japanese patients
Abstract
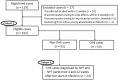
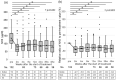
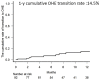
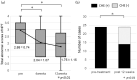
Covert hepatic encephalopathy (CHE) impairs patient quality of life and occurs in approximately 30% of liver cirrhosis (LC) cases. Japanese clinical practice guidelines recommend rifaximin to treat overt HE (OHE). However, the usefulness of rifaximin against CHE is not thoroughly investigated in Japanese patients. We aimed to investigate the efficacy of rifaximin against hyperammonemia and CHE in Japan. We observed 102 patients with HE showing hyperammonemia secondary to LC and examined various biochemical and behavioral parameters following rifaximin treatment. CHE was diagnosed when the patients exhibited two or more abnormal neuropsychological test (NPT) scores but did not indicate OHE symptoms. In the 102 cases, a significant therapeutic effect of rifaximin on hyperammonemia was observed from 2 to 48 weeks after starting treatment. Excluding 10 patients diagnosed with OHE upon starting rifaximin treatment, 12 of the 92 remaining patients (11.8%) transitioned to OHE within 1 year. The 1 year cumulative OHE transition rate was 14.5%. Among the 24 patients with CHE diagnosed by the NPT for whom NPT results could be evaluated at 4 and 12 weeks after starting treatment, 10 (41.6%) had recovered from CHE at 12 weeks. When the factors contributing to recovery from CHE were examined by multivariate analysis, an ammonia level <129 μg/dL was a significant factor. Rifaximin was thus significantly effective against both hyperammonemia and CHE in Japanese patients.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests:Professor Naoya Sakamoto received lecture fees from Bristol Myers Squibb and Pharmaceutical K.K., grants and endowments from MSD K.K. and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, and a research grant from Gilead Sciences Inc. Dr. Goki Suda received research grants from Bristol Myers Squibb. The other authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Changes in the Body Composition and Nutritional Status after Long-term Rifaximin Therapy for Hyperammonemia in Japanese Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy.Intern Med. 2020;59(20):2465-2469. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.5094-20. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 33055469 Free PMC article.
-
A simple covert hepatic encephalopathy screening model based on blood biochemical parameters in patients with cirrhosis.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 30;17(11):e0277829. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277829. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36449492 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of rifaximin, a poorly absorbed rifamycin antimicrobial agent, for hepatic encephalopathy in Japanese patients.Hepatol Res. 2021 Apr;51(4):445-460. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13622. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Hepatol Res. 2021. PMID: 33533150
-
Handgrip strength stratifies the risk of covert and overt hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2022 May;46(4):858-866. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2222. Epub 2021 Aug 23. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34287991 Review.
-
Advances in cirrhosis: Optimizing the management of hepatic encephalopathy.World J Hepatol. 2015 Dec 18;7(29):2871-9. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i29.2871. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26692331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rifaximin Alfa and Liver Diseases: More Than a Treatment for Encephalopathy, a Disease Modifier.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2023 Oct 24;19:839-851. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S425292. eCollection 2023. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2023. PMID: 37899985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiome-Liver-Brain axis in Alcohol Use Disorder. The role of gut dysbiosis and stress in alcohol-related cognitive impairment progression: possible therapeutic approaches.Neurobiol Stress. 2025 Feb 8;35:100713. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2025.100713. eCollection 2025 Mar. Neurobiol Stress. 2025. PMID: 40092632 Free PMC article.
-
Down the road towards hepatic encephalopathy. The elusive ammonia- what determines the arterial concentration?Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Dec 2;40(1):48. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01435-3. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39621139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT. Hepatic encephalopathy—definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology. 2002;35(3):716–21. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.31250 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al.. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014;60(2):715–35. doi: 10.1002/hep.27210 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bajaj JS, Cordoba J, Mullen KD, Amodio P, Shawcross DL, Butterworth RF, et al.. Review article: the design of clinical trials in hepatic encephalopathy—an International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) consensus statement. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;33(7):739–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04590.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kato A, Tanaka H, Kawaguchi T, Kanazawa H, Iwasa M, Sakaida I, et al.. Nutritional management contributes to improvement in minimal hepatic encephalopathy and quality of life in patients with liver cirrhosis: A preliminary, prospective, open-label study. Hepatol Res. 2013;43(5):452–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2012.01092.x . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

