How I treat and prevent COVID-19 in patients with hematologic malignancies and recipients of cellular therapies
- PMID: 35776899
- PMCID: PMC9249429
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022016089
How I treat and prevent COVID-19 in patients with hematologic malignancies and recipients of cellular therapies
Abstract
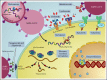
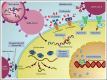
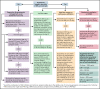
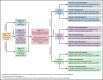
Patients with hematologic malignancies and recipients of hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) are more likely to experience severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and have a higher risk of morbidity and mortality after infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Compared with the general population, these patients have suboptimal humoral responses to COVID-19 vaccines and subsequently increased risk for breakthrough infections, underscoring the need for additional therapies, including pre- and postexposure prophylaxis, to attenuate clinical progression to severe COVID-19. Therapies for COVID-19 are mostly available for adults and in the inpatient and outpatient settings. Selection and administration of the best treatment options are based on host factors; virus factors, including circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants; and therapeutic considerations, including the clinical efficacy, availability, and practicality of treatment and its associated side effects, including drug-drug interactions. In this paper, we discuss how we approach managing COVID-19 in patients with hematologic malignancies and recipients of HCT and cell therapy.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

