HIV incidence and impact of interventions among female sex workers and their clients in the Middle East and north Africa: a modelling study
- PMID: 35777411
- PMCID: PMC9253890
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-3018(22)00100-X
HIV incidence and impact of interventions among female sex workers and their clients in the Middle East and north Africa: a modelling study
Abstract
Background: The incidence of HIV infection among female sex workers and their clients in the Middle East and north Africa is not well known. We aimed to assess HIV incidence, the contribution of heterosexual sex work networks to these numbers, and the effect of interventions by use of mathematical modelling.
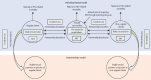
Methods: In this modelling study, we developed a novel, individual-based model to simulate HIV epidemic dynamics in heterosexual sex work networks. We applied this model to 12 countries in the Middle East and north Africa that had sufficient data to estimate incidence in 2020 and the impact of interventions by 2030 (Algeria, Bahrain, Djibouti, Iran, Libya, Morocco, Pakistan, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and Yemen). Model-input parameters were provided through a systematic review of HIV prevalence, sexual and injecting behaviours, and risk group size estimates of female sex workers and clients. Model output was number of incident HIV infections under different modelling scenarios for each country. Summary statistics were generated on these model output scenarios.
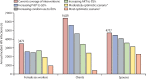
Findings: Based on the output of our model, we estimated a total of 14 604 (95% uncertainty interval [UI] CI 7929-31 819) new HIV infections in the 12 countries in 2020 among female sex workers, clients, and spouses, which constituted 28·1% of 51 995 total new cases in all adults in these 12 countries combined. Model-estimated number of new infections in 2020 in the 12 countries combined was 3471 (95% UI 1295-10 308) in female sex workers, 6416 (3144-14 223) in clients, and 4717 (3490-7288) in client spouses. Contribution of incidence in heterosexual sex work networks to total incidence varied widely, ranging from 3·3% in Pakistan to 71·8% in South Sudan and 72·7% in Djibouti. Incidence in heterosexual sex work networks was distributed roughly equally among female sex workers, clients, and client spouses. Estimated incidence rates among female sex workers per 1000 person-years ranged from 0·4 (95% UI 0·0-7·1) in Yemen to 34·3 (17·2-59·6) in South Sudan. In countries where HIV acquisition through injecting drug use creates substantial exposure for female sex workers who inject drugs, estimated incidence rates per 1000 person-years ranged from 5·1 (95% UI 0·0-35·1) in Iran to 45·8 (0·0-428·6) in Pakistan. The model output predicted that any of the programmed interventions would substantially reduce incidence. Even when a subpopulation did not benefit directly from an intervention, it benefited indirectly through reduction in onward transmission, and indirect impact was often half as large as the direct impact.
Interpretation: Substantial HIV incidence occurs in heterosexual sex work networks across the Middle East and north Africa with client spouses being heavily affected, in addition to female sex workers and clients. Rapid scaling-up of comprehensive treatment and prevention services for female sex workers is urgently needed.
Funding: Qatar National Research Fund (a member of Qatar Foundation), the Biostatistics, Epidemiology, and Biomathematics Research Core at the Weill Cornell Medicine-Qatar, Qatar University-Marubeni, the UK Medical Research Council, and the UK Department for International Development.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Simulating HIV dynamics in the Middle East and north Africa.Lancet HIV. 2022 Jul;9(7):e454-e455. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(22)00129-1. Lancet HIV. 2022. PMID: 35777405 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
HIV incidence among people who inject drugs in the Middle East and North Africa: mathematical modelling analysis.J Int AIDS Soc. 2018 Mar;21(3):e25102. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25102. J Int AIDS Soc. 2018. PMID: 29577623 Free PMC article.
-
HIV epidemiology among female sex workers and their clients in the Middle East and North Africa: systematic review, meta-analyses, and meta-regressions.BMC Med. 2019 Jun 24;17(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12916-019-1349-y. BMC Med. 2019. PMID: 31230594 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic overview of hepatitis C infection in the Middle East and North Africa.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul 21;24(27):3038-3054. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i27.3038. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30038471 Free PMC article.
-
Status of HIV and hepatitis C virus infections among prisoners in the Middle East and North Africa: review and synthesis.J Int AIDS Soc. 2016 May 27;19(1):20873. doi: 10.7448/IAS.19.1.20873. eCollection 2016. J Int AIDS Soc. 2016. PMID: 27237131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of Neisseria gonorrhoeae transmission among female sex workers and clients: A mathematical modeling study.Epidemics. 2024 Sep;48:100785. doi: 10.1016/j.epidem.2024.100785. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Epidemics. 2024. PMID: 39106639
Cited by
-
New HIV Infections Among Key Populations and Their Partners in 2010 and 2022, by World Region: A Multisources Estimation.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2024 Jan 1;95(1S):e34-e45. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003340. Epub 2024 Jan 4. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38180737 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of gonorrhea in countries of the Middle East and North Africa: systematic review, meta analyses, and meta regressions.BMC Glob Public Health. 2024 Aug 19;2(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s44263-024-00088-9. BMC Glob Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39681952 Free PMC article.
-
Agent based modelling of blood borne viruses: a scoping review.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):1411. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10271-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39695997 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus transmission among people who inject drugs in the Middle East and North Africa: mathematical modeling analyses of incidence and intervention impact.EClinicalMedicine. 2025 Jan 15;80:103040. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103040. eCollection 2025 Feb. EClinicalMedicine. 2025. PMID: 39896871 Free PMC article.
-
Trends and projection of incidence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years of HIV in the Middle East and North Africa (1990-2030).Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 24;13(1):13859. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40743-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37620356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UN Transforming our world: the 2030 agenda for sustainable development. 2015. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld
-
- UNAIDS UNAIDS 2016–2021 strategy: on the fast-track to end AIDS. 2015. http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/20151027_UNAIDS_PC...
-
- UNAIDS Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026. End inequalities. End AIDS. 2021. https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/global-AIDS-strat...
-
- UNAIDS Global HIV & AIDS statistics—fact sheet. 2021. https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet
-
- UNAIDS UNAIDS data. 2020. https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/2020_aids-data-bo...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

