Complement C3a and C3a Receptor Activation Mediates Podocyte Injuries in the Mechanism of Primary Membranous Nephropathy
- PMID: 35777783
- PMCID: PMC9529185
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2021101384
Complement C3a and C3a Receptor Activation Mediates Podocyte Injuries in the Mechanism of Primary Membranous Nephropathy
Abstract
Background: The complement system is highly activated in primary membranous nephropathy (MN). Identifying the complement components that damage podocytes has important therapeutic implications. This study investigated the role of C3a and the C3a receptor (C3aR) in the pathogenesis of MN.
Methods: C3aR expression in kidneys and circulating levels of C3a of MN patients were examined. Human podocyte damage was assessed after exposure to MN plasma +/- C3aR blockade (SB290157, JR14a). C3aR antagonists were administered to rats with Heymann nephritis on day 0 or after proteinuria. Clinical and pathologic parameters, specific IgG and complement activation, and podocyte injuries were then assessed.
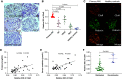
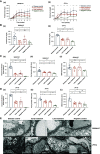
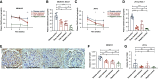
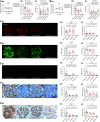
Results: In the glomeruli, C3aR staining merged well with podocin. Overexpression of C3aR correlated positively with proteinuria, serum creatinine, and no response to treatments. Human podocytes exposed to MN plasma showed increased expression of PLA2R, C3aR, and Wnt3/β-catenin, reduced expression of synaptopodin and migration function, downregulated Bcl-2, and decreased cell viability. C3aR antagonists could block these effects. In Heymann nephritis rats, C3aR blockade attenuated proteinuria, electron-dense deposition, foot process width, and glomerular basement membrane thickening in glomeruli. The increased plasma C3a levels and overexpression of C3aR were also alleviated. Specific, but not total, IgG levels decreased, with less deposition of rat IgG in glomeruli and subsequent reduction of C1q, factor B, and C5b-9.
Conclusion: C3a anaphylatoxin is a crucial effector of complement-mediated podocyte damage in MN. The C3aR antagonist may be a potentially viable treatment for this disease.
Keywords: C3a receptor; Heymann nephritis; complement; membrane nephropathy; podocyte.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Complement is Complimentary in Membranous Nephropathy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Sep;33(9):1631-1633. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2022060633. Epub 2022 Jul 13. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35831021 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Sustained activation of C3aR in a human podocyte line impairs the morphological maturation of the cells.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Dec;22(6):5326-5338. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11626. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33174024 Free PMC article.
-
C3a receptor blockade protects podocytes from injury in diabetic nephropathy.JCI Insight. 2020 Mar 12;5(5):e131849. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.131849. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32161193 Free PMC article.
-
C-reactive protein inhibits C3a/C3aR-dependent podocyte autophagy in favor of diabetic kidney disease.FASEB J. 2022 Jun;36(6):e22332. doi: 10.1096/fj.202200198R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35503088
-
A podocyte view of membranous nephropathy: from Heymann nephritis to the childhood human disease.Pflugers Arch. 2017 Aug;469(7-8):997-1005. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2007-x. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 28597189 Review.
-
Membranous nephropathy.Contrib Nephrol. 2011;169:107-125. doi: 10.1159/000313948. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21252514 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathological mechanism of immune disorders in diabetic kidney disease and intervention strategies.World J Diabetes. 2024 Jun 15;15(6):1111-1121. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1111. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38983817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effect of compound K against podocyte injury in chronic kidney disease by maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84704-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39748100 Free PMC article.
-
Complement System Inhibitors in Nephrology: An Update-Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 19;26(12):5902. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125902. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the complement system in primary membranous nephropathy: A narrative review in the era of new therapeutic targets.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 24;13:1009864. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1009864. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36353636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune podocytes in the immune microenvironment of lupus nephritis (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2023 Nov;28(5):204. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13091. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37711069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

