Mapping Research Domain Criteria using a transdiagnostic mini-RDoC assessment in mental disorders: a confirmatory factor analysis
- PMID: 35778521
- PMCID: PMC10085934
- DOI: 10.1007/s00406-022-01440-6
Mapping Research Domain Criteria using a transdiagnostic mini-RDoC assessment in mental disorders: a confirmatory factor analysis
Abstract
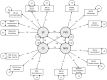
This study aimed to build on the relationship of well-established self-report and behavioral assessments to the latent constructs positive (PVS) and negative valence systems (NVS), cognitive systems (CS), and social processes (SP) of the Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) framework in a large transnosological population which cuts across DSM/ICD-10 disorder criteria categories. One thousand four hundred and thirty one participants (42.1% suffering from anxiety/fear-related, 18.2% from depressive, 7.9% from schizophrenia spectrum, 7.5% from bipolar, 3.4% from autism spectrum, 2.2% from other disorders, 18.4% healthy controls, and 0.2% with no diagnosis specified) recruited in studies within the German research network for mental disorders for the Phenotypic, Diagnostic and Clinical Domain Assessment Network Germany (PD-CAN) were examined with a Mini-RDoC-Assessment including behavioral and self-report measures. The respective data was analyzed with confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to delineate the underlying latent RDoC-structure. A revised four-factor model reflecting the core domains positive and negative valence systems as well as cognitive systems and social processes showed a good fit across this sample and showed significantly better fit compared to a one factor solution. The connections between the domains PVS, NVS and SP could be substantiated, indicating a universal latent structure spanning across known nosological entities. This study is the first to give an impression on the latent structure and intercorrelations between four core Research Domain Criteria in a transnosological sample. We emphasize the possibility of using already existing and well validated self-report and behavioral measurements to capture aspects of the latent structure informed by the RDoC matrix.
Keywords: Confirmatory factor analysis CFA; Diagnosis and classification; PD-CAN; RDoC; Research Domain Criteria; Transdiagnostic.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Andreas Meyer-Lindenberg received the following incomes: consultancy: Boehringer Ingelheim, Elsevier, Brainsway, Lundbeck Int. Neuroscience Foundation, Lundbeck A/S, The Wolfson Foundation, Bloomfield Holding Ltd, Shanghai Research Center for Brain Science, Thieme Verlag, Sage Therapeutics, v Behring Röntgen Stiftung, Fondation FondaMental, Janssen-Cilag GmbH, MedinCell, Brain Mind Institute, Agence Nationale de la Recherche, CISSN (Catania Internat. Summer School of Neuroscience), Daimler und Benz Stiftung, American Association for the Advancement of Science; Speaker fees: Italian Society of Biological Psychiatry, Merz-Stiftung, Forum Werkstatt Karlsruhe, Lundbeck SAS France, BAG Psychiatrie Oberbayern, Klinik für Psychiatrie und Psychotherapie Ingolstadt, med Update GmbH, Society of Biological Psychiatry, Siemens Healthineers. The present work is unrelated to these relationships. Frank Padberg is a member of the European Scientific Advisory Board of Brainsway Inc., Jerusalem, Israel, and has received speaker’s honoraria from Mag&More GmbH and the neuroCare Group. His lab has received support with equipment from neuroConn GmbH, Ilmenau, Germany, and Mag & More GmbH and Brainsway Inc., Jerusalem, Israel. Dr. Banaschewski served in an advisory or consultancy role for ADHS digital, Infectopharm, Lundbeck, Medice, Neurim Pharmaceuticals, Oberberg GmbH, Roche, and Takeda. He received conference support or speaker’s fee by Medice and Takeda. He received royalties from Hogrefe, Kohlhammer, CIP Medien, Oxford University Press; the present work is unrelated to these relationships. Michael Bauer has served on advisory boards in the past 3 years for Janssen-Cilag, GH Research, Takeda, Novartis, Sunovion, neuraxpharm, Shire International GmbH, and Sumitomo Dainippon; he received honoraria for lectures by Hexal AG, Janssen-Cilag, neuraxpharm, Sumitomo Dainippon. Dr. Rupprecht served as advisor for SAGE Inc. and GABA Therapeutics. All other authors report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders DSM-5. 5. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
-
- World Health Organization . International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems, 10th revision. 5. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

