Automated image curation in diabetic retinopathy screening using deep learning
- PMID: 35778615
- PMCID: PMC9249740
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-15491-1
Automated image curation in diabetic retinopathy screening using deep learning
Abstract
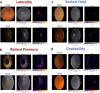
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) screening images are heterogeneous and contain undesirable non-retinal, incorrect field and ungradable samples which require curation, a laborious task to perform manually. We developed and validated single and multi-output laterality, retinal presence, retinal field and gradability classification deep learning (DL) models for automated curation. The internal dataset comprised of 7743 images from DR screening (UK) with 1479 external test images (Portugal and Paraguay). Internal vs external multi-output laterality AUROC were right (0.994 vs 0.905), left (0.994 vs 0.911) and unidentifiable (0.996 vs 0.680). Retinal presence AUROC were (1.000 vs 1.000). Retinal field AUROC were macula (0.994 vs 0.955), nasal (0.995 vs 0.962) and other retinal field (0.997 vs 0.944). Gradability AUROC were (0.985 vs 0.918). DL effectively detects laterality, retinal presence, retinal field and gradability of DR screening images with generalisation between centres and populations. DL models could be used for automated image curation within DR screening.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
P Nderitu, JM Nunez do Rio, L Webster, SS Mann, D Hopkins, MJ Cardoso, M Modat, C Bergeles has no conflicts of interest to declare. T Jacksons’ employer (King’s College Hospital) receives funding for participants enrolled on commercial clinical trials of diabetic retinopathy including THR149-002 (sponsor: OXURION), NEON NPDR (sponsor: BAYER), RHONE-X (sponsor: ROCHE) and ALTIMETER (sponsor: ROCHE). He has been paid for an expert clinical opinion by Kirkland and Ellis Solicitors, acting for REGENERON.
Figures




References
-
- IDF. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Ninth Edition. (2019).
-
- Blindness, G. B. D. Vision Impairment, C. Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease, S Causes of blindness and vision impairment in 2020 and trends over 30 years, and prevalence of avoidable blindness in relation to VISION 2020: The Right to Sight: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet Glob. Health. 2021;9:e144–e160. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30489-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

