The association and mediation role of Food and Nutrition Literacy (FNLIT) with eating behaviors, academic achievement and overweight in 10-12 years old students: a structural equation modeling
- PMID: 35778743
- PMCID: PMC9248125
- DOI: 10.1186/s12937-022-00796-8
The association and mediation role of Food and Nutrition Literacy (FNLIT) with eating behaviors, academic achievement and overweight in 10-12 years old students: a structural equation modeling
Abstract
Background: Food and nutrition literacy is a key factor in shaping healthy dietary behaviors and may result in decreasing decrease the prevalence of overweight. Empirical research on food and nutrition literacy and its outcomes is limited, especially among children and adolescents. Thus, this study investigates the link between Food and Nutrition Literacy (FNLIT) with eating behaviors, academic performance, and overweight in 10-12 years old students in Tehran, Iran.
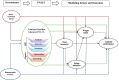
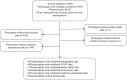
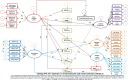
Methods: This study was performed through two phases: 1) Proposing a conceptual model of the relationship between FNLIT and its determinants and outcomes, based on the existing evidence and previous models, and 2) Testing the proposed FNLIT model through a cross-sectional study on 803 primary school students (419 boys and 384 girls, from 34 public and 10 private primary schools), aged 10-12 years using structural equation modeling. Demographic, socio-economic, and household food security characteristics were collected by interviewing the students and their mothers/caregivers using a questionnaire. FNLIT was measured by a self-administered, locally designed, and validated questionnaire.
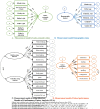
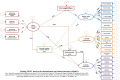
Results: The fit indices suggested a reasonably adequate fit of the data to the hypothesized model (χ2/df = 2.03, p < 0.001, goodness of fit index (GFI) = 0.90, adjusted goodness of fit index (AGFI) = 0.88, comparative fit index (CFI) = 0.91, incremental fit index (IFI) = 0.91, root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) = 0.04, standardized root mean residual (SRMR) = 0.06). SES was directly and positively related to FNLIT and its subscale in students. FNLIT score had a positive direct (non-mediated) relationship with healthy eating behavior and academic performance. This pattern was strongly reversed in unhealthy eating behavior. There was a full mediation relationship between FNLIT and overweight/obesity via healthy eating behaviors. SES predicted academic performance partially through the mediating effect of Food Label Literacy (FLL). The results indicated that despite the direct relationship between SES and academic performance, an indirect but negative relationship existed with food insecurity. The finding also revealed the fully mediating role of Food Choice Literacy (FCL) in the relationship between demographic factors and healthy eating behaviors. Our study also found that Interactive Food and Nutrition Literacy (IFNL) protected unhealthy eating behaviors, and FCL predicted healthy eating behaviors in children.
Conclusion: Our study draws attention to FNLIT, especially the skills domain, including IFNL, FCL, and FLL, as the most important determinant of healthy eating behavior, academic performance, and weight status in school-age children reduces social inequalities in children's development. To ensure an adequate level of FNLIT, educators should assess and plan to enhance food literacy skills in children and adolescents.
Keywords: Academic performance; Eating behavior; Elementary school children; Food and nutrition literacy; Food security; Structural Equation Model.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Colatruglio S, Slater J. Food literacy: bridging the gap between food, nutrition and well being. In: Deer F, Falkenberg T, McMillan B, Sims L, editors. Sustainable well-being: concepts, issues, and educational practices. Winnipeg: ESWB Press; 2014. pp. 37–55.
-
- Laska MN, Larson NI, Neumark-Sztainer D, Story M. Does involvement in food preparation track from adolescence to young adulthood and is it associated with better dietary quality? Findings from a 10-year longitudinal study. Public Health Nutr. 2012;15:1150–1158. doi: 10.1017/S1368980011003004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zoellner J, You W, Connell C, Smith-Ray RL, Allen K, Tucker KL, Davy BM, Estabrooks P. Health literacy is associated with healthy eating index scores and sugar-sweetened beverage intake: findings from the rural Lower Mississippi Delta. J Am Diet Assoc. 2011;111:1012–1020. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2011.04.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

