The actions and interactions of family genetic risk scores for alcohol use disorder and major depression on the risk for these two disorders
- PMID: 35779072
- PMCID: PMC10016432
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32909
The actions and interactions of family genetic risk scores for alcohol use disorder and major depression on the risk for these two disorders
Abstract
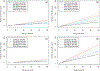
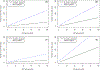
We know little about how genetic risk factors for two disorders jointly act and interact in predisposing to illness. Therefore, in the Swedish population, born 1970-1990 (n = 2,116,082) and followed through 2015, we examine, using additive Cox models, the impact of the family genetic risk scores (FGRS) for alcohol use disorder (AUD) and major depression (MD), their interaction with each other and with the relevant comorbid disorder on risk for AUD and MD. FGRS scores are constructed using rates of illness in first-fourth degree relatives. FGRS for AUD and MD interacted in predicting of both disorders and one FRGS (e.g., for AUD) interacted with the phenotype of MD to predict that disorder (e.g., AUD). These FGRS interactions were not substantially attenuated by adding interactions with the disorders. These results replicated across sexes. In predicting risk for a given disorder, we rarely consider genetic liabilities for other disorders. But such effects were here significant and interactive. Furthermore, the primary disorder genetic risk interacts with comorbid disorders. The pathways to risk for disorders from their and other disorders' genetic liability may be more complex than commonly considered.
Keywords: alcohol use disorder; family genetic risk score; interactions; major depression.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

