OsPP65 Negatively Regulates Osmotic and Salt Stress Responses Through Regulating Phytohormone and Raffinose Family Oligosaccharide Metabolic Pathways in Rice
- PMID: 35779169
- PMCID: PMC9250576
- DOI: 10.1186/s12284-022-00581-5
OsPP65 Negatively Regulates Osmotic and Salt Stress Responses Through Regulating Phytohormone and Raffinose Family Oligosaccharide Metabolic Pathways in Rice
Abstract
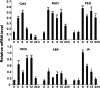
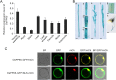
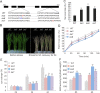
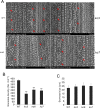
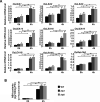
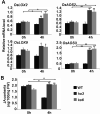
Although type 2C protein phosphatases (PP2Cs) have been demonstrated to play important roles in regulating plant development and various stress responses, their specific roles in rice abiotic stress tolerance are still largely unknown. In this study, the functions of OsPP65 in rice osmotic and salt stress tolerance were investigated. Here, we report that OsPP65 is responsive to multiple stresses and is remarkably induced by osmotic and salt stress treatments. OsPP65 was highly expressed in rice seedlings and leaves and localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm. OsPP65 knockout rice plants showed enhanced tolerance to osmotic and salt stresses. Significantly higher induction of genes involved in jasmonic acid (JA) and abscisic acid (ABA) biosynthesis or signaling, as well as higher contents of endogenous JA and ABA, were observed in the OsPP65 knockout plants compared with the wild-type plants after osmotic stress treatment. Further analysis indicated that JA and ABA function independently in osmotic stress tolerance conferred by loss of OsPP65. Moreover, metabolomics analysis revealed higher endogenous levels of galactose and galactinol but a lower content of raffinose in the OsPP65 knockout plants than in the wild-type plants after osmotic stress treatment. These results together suggest that OsPP65 negatively regulates osmotic and salt stress tolerance through regulation of the JA and ABA signaling pathways and modulation of the raffinose family oligosaccharide metabolism pathway in rice. OsPP65 is a promising target for improvement of rice stress tolerance using gene editing.
Keywords: ABA; JA; Osmotic stress tolerance; PP2C; Raffinose family oligosaccharide; Rice.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interruption of Jasmonic Acid Biosynthesis Causes Differential Responses in the Roots and Shoots of Maize Seedlings against Salt Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 9;20(24):6202. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246202. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31835299 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulose synthase-like protein OsCSLD4 plays an important role in the response of rice to salt stress by mediating abscisic acid biosynthesis to regulate osmotic stress tolerance.Plant Biotechnol J. 2022 Mar;20(3):468-484. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13729. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Plant Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 34664356 Free PMC article.
-
Wheat bHLH-type transcription factor gene TabHLH1 is crucial in mediating osmotic stresses tolerance through modulating largely the ABA-associated pathway.Plant Cell Rep. 2016 Nov;35(11):2309-2323. doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-2036-5. Epub 2016 Aug 19. Plant Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27541276
-
Protein Phosphatase Type 2C Functions in Phytohormone-Dependent Pathways and in Plant Responses to Abiotic Stresses.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021;22(5):430-440. doi: 10.2174/1389203722666210322144442. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021. PMID: 33749560 Review.
-
How Plants Tolerate Salt Stress.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jul 15;45(7):5914-5934. doi: 10.3390/cimb45070374. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37504290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Bioactive Substances in Fruits of Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliott Exposed to Combined Light-Type, Chitosan Oligosaccharide, and Spent Mushroom Residue Treatments.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 30;12(3):604. doi: 10.3390/plants12030604. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771688 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing raffinose family oligosaccharides content in plants: A tightrope walk.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 28;14:1134754. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1134754. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37056499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of PP2C Gene Family in Eelgrass.Genes (Basel). 2025 May 29;16(6):657. doi: 10.3390/genes16060657. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565549 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Molecular Aspects and Integrated Omics Strategies for Understanding the Abiotic Stress Tolerance of Rice.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 18;12(10):2019. doi: 10.3390/plants12102019. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37653936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Alternative Splicing Profile of the Raffinose synthase Gene in Grass Species.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 5;24(13):11120. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311120. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelgawad ZA, Khalafaallah AA, Abdallah MM. Impact of methyl jasmonate on antioxidant activity and some biochemical aspects of maize plant grown under water stress condition. Agric Sci. 2014;5(12):1077–1088.
-
- Bandurska H, Stroin´ski A, Kubis´ J, The effect of jasmonic acid on the accumulation of ABA, proline and spermidine and its influence on membrane injury under water deficit in two barley genotypes. Acta Physiol Plant. 2003;25:279–285. doi: 10.1007/s11738-003-0009-0. - DOI
-
- Cheng W, Endo A, Zhou L, Penney J, Chen H, Arroyo A, Leon P, Nambara E, Asami T, Seo M, Koshiba T, Sheen J. A unique short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase in Arabidopsis glucose signaling and abscisic acid biosynthesis and functions. Plant Cell. 2002;14(11):2723–2743. doi: 10.1105/tpc.006494. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2021A1515011107/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- R2020PY-JX001/Special Fund for Scientific Innovation Strategy-Construction of High Level Academy of Agriculture Science
- R2020PY-JX019/Special Fund for Scientific Innovation Strategy-Construction of High Level Academy of Agriculture Science
- Governor's Special Program 2018-2019/Special Program for Crop Germplasm Resources of Guangdong Province
- 272 of 2021/The investment project of Department of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Development and Reform Commission, Guangdong province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

