Transketolase in human Müller cells is critical to resist light stress through the pentose phosphate and NRF2 pathways
- PMID: 35779441
- PMCID: PMC9287732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102379
Transketolase in human Müller cells is critical to resist light stress through the pentose phosphate and NRF2 pathways
Abstract
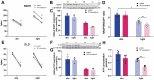
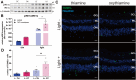
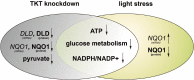
The Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP), a metabolic offshoot of the glycolytic pathway, provides protective metabolites and molecules essential for cell redox balance and survival. Transketolase (TKT) is the critical enzyme that controls the extent of "traffic flow" through the PPP. Here, we explored the role of TKT in maintaining the health of the human retina. We found that Müller cells were the primary retinal cell type expressing TKT in the human retina. We further explored the role of TKT in human Müller cells by knocking down its expression in primary cultured Müller cells (huPMCs), isolated from the human retina (11 human donors in total), under light-induced oxidative stress. TKT knockdown and light stress reduced TKT enzymatic activities and the overall metabolic activities of huPMCs with no detectable cell death. TKT knockdown restrained the PPP traffic flow, reduced the expression of NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1), impaired the antioxidative response of NRF2 to light stress and aggravated the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. TKT knockdown also inhibited overall glucose intake, reduced expression of Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DLD) and impaired the energy supply of the huPMCs. In summary, Müller cell-mediated TKT activity plays a critical protective role in the stressed retina. Knockdown of TKT disrupted the PPP and impaired overall glucose utilisation by huPMCs and rendered huPMCs more vulnerable to light stress by impairing energy supply and antioxidative NRF2 responses.
Keywords: Müller cells; NQO1; NRF2; Oxidative stress; Pentose phosphate pathway; Transketolase (TKT).
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Reichenbach A., Bringmann A. Glia of the human retina. Glia. 2020;68(4):768–796. - PubMed
-
- Reichenbach A., Bringmann A. New functions of Muller cells. Glia. 2013;61(5):651–678. - PubMed
-
- Coorey N.J., Shen W., Chung S.H., Zhu L., Gillies M.C. The role of glia in retinal vascular disease. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2012;95(3):266–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

