Association of triglyceride-glucose index with prognosis of COVID-19: A population-based study
- PMID: 35779467
- PMCID: PMC9225941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.06.014
Association of triglyceride-glucose index with prognosis of COVID-19: A population-based study
Abstract
Background: Triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is a simple and reliable surrogate marker for insulin resistance. Epidemiology studies have shown that insulin resistance is a risk factor for various infectious diseases. We evaluated the prognostic value of TyG index measured before the COVID-19 infection in COVID-19 infected patients.
Methods: From a nationwide COVID-19 cohort dataset in Korea, we included COVID-19 patients diagnosed between Jan and Jun 2020. Based on the nationwide health screening data between 2015 and 2018, TyG index was calculated as ln [triglyceride (mg/dL) × fasting glucose level (mg/dL)/2]. Primary outcome is development of severe complications of COVID-19 defined as composite of mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit care, high-flow oxygen therapy, and mortality within two months after the diagnosis of COVID-19.
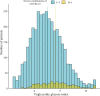
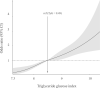
Results: This study included 3887 patients with COVID-19 confirmed by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Mean ± standard deviation of TyG index was 8.54 ± 0.61. Severe complications of COVID-19 were noted in 289 (7.44%) patients. In the multivariate logistic regression, TyG index was positively associated with severe complications of COVID-19 (adjusted odds ratio: 1.42, 95% confidence interval [1.12-1.79]).
Conclusions: In COVID-19 infected patients, high TyG index was associated with increased risk for severe complications. TyG index might be useful predictor for the severity of COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; Glucose; Insulin resistance; Triglyceride-glucose index.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

