Antinociceptive and Analgesic Effects of (2 R,6 R)-Hydroxynorketamine
- PMID: 35779947
- PMCID: PMC9426759
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.122.001278
Antinociceptive and Analgesic Effects of (2 R,6 R)-Hydroxynorketamine
Abstract
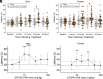
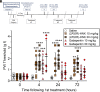
Commonly used pain therapeutics, such as opioid medications, exert dangerous side effects and lack effectiveness in treating some types of pain. Ketamine is also used to treat pain, but side effects limit its widespread use. (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine (HNK) is a ketamine metabolite that potentially shares some beneficial behavioral effects of its parent drug without causing significant side effects. This study compared the profile and potential mechanisms mediating the antinociception activity of ketamine and (2R,6R)-HNK in C57BL/6J mice. Additionally, this study compared the reversal of mechanical allodynia by (2R,6R)-HNK with gabapentin in a model of neuropathic pain. Unlike the near-immediate and short-lived antinociception caused by ketamine, (2R,6R)-HNK produced late-developing antinociception 24 hours following administration. Pharmacological blockade of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors with 2,3-dioxo-6-nitro-7-sulfamoyl-benzo[f]quinoxaline (NBQX) prevented the initiation and expressionof (2R,6R)-HNK antinociception, suggesting the involvement of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptor-dependent glutamatergic mechanisms in the pain reduction-like responses. Blockade of opioid receptors with naltrexone partially prevented the antinociceptive effect of ketamine but was ineffective against (2R,6R)-HNK. Furthermore, (2R,6R)-HNK did not produce dystaxia, even when tested at doses five times greater than those needed to produce antinociception, indicating a superior safety profile for (2R,6R)-HNK over ketamine. Additionally, (2R,6R)-HNK reversed mechanical allodynia in a spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain with similar short-term efficacy to gabapentin (within 4 hours) while outperforming gabapentin 24 hours after administration. These findings support the further study of (2R,6R)-HNK as a potentially valuable agent for treating different types of pain and establish certain advantages of (2R,6R)-HNK treatment over ketamine and gabapentin in corresponding assays for pain. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: The ketamine metabolite (2R,6R)-HNK produced antinociception in male and female mice 24 hours after administration via activation of AMPA receptors. The effects of (2R,6R)-HNK differed in time course and mechanism and presented a better safety profile than ketamine. (2R,6R)-HNK also reversed allodynia in SNI-operated animals within 4 hours of treatment onset, with a duration of effect lasting longer than gabapentin. Taken together, (2R,6R)-HNK demonstrates the potential for development as a non-opioid analgesic drug.
U.S. Government work not protected by U.S. copyright.
Figures
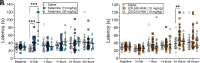

References
-
- Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, Krystal JH (2000) Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47:351–354. - PubMed
-
- Berryman ER, Harris RL, Moalli M, Bagi CM (2009) Digigait quantitation of gait dynamics in rat rheumatoid arthritis model. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 9:89–98. - PubMed
-
- Bourquin A-F, Süveges M, Pertin M, Gilliard N, Sardy S, Davison AC, Spahn DR, Decosterd I (2006) Assessment and analysis of mechanical allodynia-like behavior induced by spared nerve injury (SNI) in the mouse. Pain 122:14. e1–14. - PubMed
-
- Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

