SP1 Promotes HDAC4 Expression and Inhibits HMGB1 Expression to Reduce Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammatory Response after Sepsis
- PMID: 35780770
- PMCID: PMC9274949
- DOI: 10.1159/000518277
SP1 Promotes HDAC4 Expression and Inhibits HMGB1 Expression to Reduce Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammatory Response after Sepsis
Abstract
As a serious and elusive syndrome caused by infection, sepsis causes a high rate of mortality around the world. Our investigation aims at exploring the role and possible mechanism of specificity protein-1 (SP1) in the development of sepsis. A mouse model of sepsis was established by cecal ligation perforation, and a cellular model was stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), followed by determination of the SP1 expression. It was determined that SP1 was poorly expressed in the intestinal tissues of septic mice and LPS-treated cells. Next, we examined the interactions among SP1, histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4), and high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and found that SP1 bound to the HDAC4 promoter to upregulate its expression, thereby promoting the deacetylation of HMGB1. Meanwhile, gain- or loss-of-function approaches were applied to evaluate the intestinal barrier dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammatory response. Overexpression of SP1 or underexpression of HMGB1 was observed to reduce intestinal barrier dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammatory injury. Collectively, these experimental data provide evidence reporting that SP1 could promote the HDAC4-mediated HMGB1 deacetylation to reduce intestinal barrier dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammatory response induced by sepsis, providing a novel therapeutic target for sepsis prevention and treatment.
Keywords: High mobility group box 1; Histone deacetylase 4; Inflammatory response; Intestinal barrier dysfunction; Oxidative stress; Sepsis; Specificity protein-1.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures


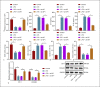

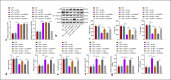


Similar articles
-
Biapenem reduces sepsis mortality via barrier protective pathways against HMGB1-mediated septic responses.Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Jun;73(3):786-795. doi: 10.1007/s43440-020-00212-0. Epub 2021 Jan 30. Pharmacol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33515401
-
Inhibitory functions of maslinic acid, a natural triterpene, on HMGB1-mediated septic responses.Phytomedicine. 2020 Apr;69:153200. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153200. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32163831
-
Barrier protective functions of hederacolchiside-E against HMGB1-mediated septic responses.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jan;163:105318. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105318. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33246171
-
[Basic research in sepsis: advances and challenges].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Jun;36(6):561-566. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240326-00287. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 38991952 Review. Chinese.
-
The Protective Effect of Octanoic Acid on Sepsis: A Review.Nutr Rev. 2025 Mar 1;83(3):e1270-e1285. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuae106. Nutr Rev. 2025. PMID: 39101596 Review.
Cited by
-
m6A demethylase FTO transcriptionally activated by SP1 improves ischemia reperfusion-triggered acute kidney injury by activating Ambra1/ULK1-mediated autophagy.FASEB J. 2024 Oct 31;38(20):e70118. doi: 10.1096/fj.202400132RRR. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 39439252 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms and functions of protein acetylation in sepsis and sepsis-associated organ dysfunction.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jul 26;30(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00773-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40713493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and verification of disulfidptosis-related genes in sepsis-induced acute lung injury.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 28;11:1430252. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1430252. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39262873 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc-Dependent Histone Deacetylases in Lung Endothelial Pathobiology.Biomolecules. 2024 Jan 23;14(2):140. doi: 10.3390/biom14020140. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
circ-0001875 downregulation is associated with M1 macrophage activation and lung inflammation in severe asthma.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 30;16:1601272. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1601272. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40661956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taeb AM, Hooper MH, Marik PE. Sepsis: current definition, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017;32((3)):296–308. - PubMed
-
- Xie S, Yang T, Wang Z, Li M, Ding L, Hu X, et al. Astragaloside IV attenuates sepsis-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction via suppressing RhoA/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;78:106066. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S, Tripathy S, Jyoti A, Singh SG. Recent advances in biosensors for diagnosis and detection of sepsis: a comprehensive review. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;124–125:205–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

