The Antifibrotic Effects of Inhaled Treprostinil: An Emerging Option for ILD
- PMID: 35781186
- PMCID: PMC9402520
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-022-02229-8
The Antifibrotic Effects of Inhaled Treprostinil: An Emerging Option for ILD
Abstract
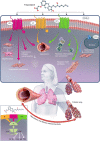
Interstitial lung diseases (ILD) encompasses a heterogeneous group of parenchymal lung diseases characterized by variable amounts of inflammation and fibrosis. The targeting of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts with antifibrotic treatments is a potential therapeutic target for these potentially fatal diseases. Treprostinil is unique among the prostacyclin mimetics in that it has distinct actions at additional prostaglandin receptors. Preclinical and clinical evidence suggests that treprostinil has antifibrotic effects through the activation of the prostaglandin E receptor 2 (EP2), the prostaglandin D receptor 1 (DP1), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR). In vivo studies of EP2 and the DP1 have found that administration of treprostinil resulted in a reduction in cell proliferation, reduced collagen secretion and synthesis, and reduced lung inflammation and fibrosis. In vitro and in vivo studies of PPARβ and PPARγ demonstrated that treprostinil inhibited fibroblast proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Clinical data from a post hoc analysis of the INCREASE trial found that inhaled treprostinil improved forced vital capacity in the overall population as well as in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis subgroups. These preclinical and clinical findings suggest a dual benefit of treprostinil through the amelioration of both lung fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension.
Keywords: Antifibrotic; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Interstitial lung diseases; Pulmonary fibrosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhaled treprostinil and forced vital capacity in patients with interstitial lung disease and associated pulmonary hypertension: a post-hoc analysis of the INCREASE study.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Nov;9(11):1266-1274. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00165-X. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 34214475 Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic administration of inhaled INS1009, a treprostinil prodrug formulation, inhibits bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Apr;49:95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2018.01.012. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29408757
-
Role of prostacyclin versus peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta receptors in prostacyclin sensing by lung fibroblasts.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006 Feb;34(2):242-6. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0289OC. Epub 2005 Oct 20. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16239641
-
The potential for inhaled treprostinil in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2011 Jun;5(3):195-206. doi: 10.1177/1753465810397693. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2011. PMID: 21300738 Review.
-
The mechanistic basis of prostacyclin and its stable analogues in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Role of membrane versus nuclear receptors.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015 Jul;120:56-71. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2015.04.007. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015. PMID: 25917921 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhaled treprostinil in group 3 pulmonary hypertension associated with lung disease: results of the INCREASE and PERFECT studies.Breathe (Sheff). 2025 Mar 18;21(1):240242. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0242-2024. eCollection 2025 Jan. Breathe (Sheff). 2025. PMID: 40104254 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion syndrome and its effect on the cardiovascular system: The role of treprostinil, a synthetic prostacyclin analog.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023 Sep 27;15(9):1858-1870. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i9.1858. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023. PMID: 37901735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The complement cascade in lung injury and disease.Respir Res. 2024 Jan 4;25(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02657-2. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38178176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary Hypertension in the Course of Interstitial Lung Diseases-A Personalised Approach Is Needed to Identify a Dominant Cause and Provide an Effective Therapy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 13;13(14):2354. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13142354. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Treprostinil Inhalation Powder for Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Evidence to Date.Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2024 Jun 5;16:51-59. doi: 10.2147/DHPS.S372239. eCollection 2024. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2024. PMID: 38855777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement: update of the International Multidisciplinary Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188(6):733–748. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

