Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Fostamatinib and Its Active Moiety R406
- PMID: 35781630
- PMCID: PMC9250994
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-022-01135-0
Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Fostamatinib and Its Active Moiety R406
Abstract
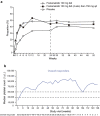
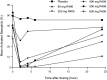
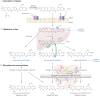
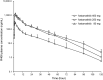
Fostamatinib is the first approved spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor for chronic immune thrombocytopenia. This review summarizes the clinical development, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, drug-drug interactions, adverse events, and comprehensive analyses of fostamatinib. While integrating these findings, we discuss the fostering and improvement of fostamatinib for further clinical applications. Fostamatinib is designed as a prodrug and cleavage of its active moiety R406 in the intestine. As R406 is the major product in the blood, this review mainly discusses the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of R406. It is metabolized by cytochrome 3A4 and UGT1A9 in the liver and is dominantly excreted in feces after anaerobic modification by the gut microbiota. As fostamatinib and R406 strongly inhibit the breast cancer resistance protein, the interaction with those substrates, particularly statins, should be carefully monitored. In patients with immune thrombocytopenia, fostamatinib administration started at 100 mg twice daily, and most patients increased to 150 mg twice daily in the clinical trial. Although responders showed a higher R406 concentration than non-responders, the correlation between R406 exposure and achievement of the platelet count as a pharmacodynamic marker was uncertain in the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis. Additionally, R406 concentration was almost halved in patients with a heavy body weight; hence, the exposure-efficacy study for suitable dosing should be continued with post-marketing data. In contrast, the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis for exposure safety revealed that R406 exposure significantly correlated with the incidence of hypertension. Even though the influence of elevated exposure on other toxicities, including diarrhea and neutropenia, is still unclear, careful management is required with dose escalation to avoid toxicity-related discontinuation.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of fostamatinib in refractory immune thrombocytopenia: a meta-analysis from randomized controlled trials.Ann Hematol. 2024 Sep;103(9):3357-3368. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05824-7. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38856778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the disposition of fostamatinib in Japanese subjects including pharmacokinetic assessment in dry blood spots: results from two phase I clinical studies.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Jan;72(1):61-71. doi: 10.1007/s00228-015-1961-5. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26490353 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics of fostamatinib, a spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) inhibitor, in healthy human subjects following single and multiple oral dosing in three phase I studies.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Jul;76(1):78-88. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12048. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23190017 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Metabolism of fostamatinib, the oral methylene phosphate prodrug of the spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor R406 in humans: contribution of hepatic and gut bacterial processes to the overall biotransformation.Drug Metab Dispos. 2010 Jul;38(7):1166-76. doi: 10.1124/dmd.110.032151. Epub 2010 Apr 6. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010. PMID: 20371637
-
Fostamatinib: a review of its clinical efficacy and safety in the management of chronic adult immune thrombocytopenia.Immunotherapy. 2020 Dec;12(18):1325-1340. doi: 10.2217/imt-2020-0215. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Immunotherapy. 2020. PMID: 33023353 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Sovleplenib, a Selective Inhibitor of Syk in Clinical Development for Autoimmune Diseases and Cancers.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024 Apr 18;15(5):595-601. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00553. eCollection 2024 May 9. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024. PMID: 38746892 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Syk and BTK Inhibitors in Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Comprehensive Review of Emerging Evidence.Mediators Inflamm. 2025 May 9;2025:5578929. doi: 10.1155/mi/5578929. eCollection 2025. Mediators Inflamm. 2025. PMID: 40385351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting host kinases to combat dengue virus infection and disease.Antiviral Res. 2025 Sep;241:106172. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2025.106172. Epub 2025 May 8. Antiviral Res. 2025. PMID: 40348023 Review.
-
Spleen tyrosine kinase: a novel pharmacological target for sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and multi-organ failure.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 4;15:1447901. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447901. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39559354 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of fostamatinib in refractory immune thrombocytopenia: a meta-analysis from randomized controlled trials.Ann Hematol. 2024 Sep;103(9):3357-3368. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05824-7. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38856778 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

