In situ autofluorescence lifetime assay of a photoreceptor stimulus response in mouse retina and human retinal organoids
- PMID: 35781966
- PMCID: PMC9208582
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.455783
In situ autofluorescence lifetime assay of a photoreceptor stimulus response in mouse retina and human retinal organoids
Abstract
Photoreceptors are the key functional cell types responsible for the initiation of vision in the retina. Phototransduction involves isomerization and conversion of vitamin A compounds, known as retinoids, and their recycling through the visual cycle. We demonstrate a functional readout of the visual cycle in photoreceptors within stem cell-derived retinal organoids and mouse retinal explants based on spectral and lifetime changes in autofluorescence of the visual cycle retinoids after exposure to light or chemical stimuli. We also apply a simultaneous two- and three-photon excitation method that provides specific signals and increases contrast between these retinoids, allowing for reliable detection of their presence and conversion within photoreceptors. This multiphoton imaging technique resolves the slow dynamics of visual cycle reactions and can enable high-throughput functional screening of retinal tissues and organoid cultures with single-cell resolution.
© 2022 Optica Publishing Group under the terms of the Optica Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
D.M.G. has an ownership interest in Opsis Therapeutics LLC, which has licensed the technology to generate retinal organoids from pluripotent stem cell sources referenced in this publication. D.M.G. also declared intellectual rights through the Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation and a consultant role with FUJIFILM Cellular Dynamics International. All other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures


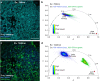
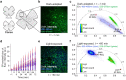

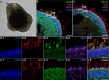
References
-
- Meyer J. S., Shearer R. L., Capowski E. E., Wright L. S., Wallace K. A., McMillan E. L., Zhang S. C., Gamm D. M., “Modeling early retinal development with human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106(39), 16698–16703 (2009).10.1073/pnas.0905245106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Cordero A., Kruczek K., Naeem A., Fernando M., Kloc M., Ribeiro J., Goh D., Duran Y., Blackford S. J. I., Abelleira-Hervas L., Sampson R. D., Shum I. O., Branch M. J., Gardner P. J., Sowden J. C., Bainbridge J. W. B., Smith A. J., West E. L., Pearson R. A., Ali R. R., “Recapitulation of Human Retinal Development from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Generates Transplantable Populations of Cone Photoreceptors,” Stem Cell Rep. 9(3), 820–837 (2017).10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.07.022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li L., Zhao H., Xie H., Akhtar T., Yao Y., Cai Y., Dong K., Gu Y., Bao J., Chen J., Zhang M., Zhong K., Xu W., Xue T., “Electrophysiological characterization of photoreceptor-like cells in human inducible pluripotent stem cell-derived retinal organoids during in vitro maturation,” Stem Cells 39(7), 959–974 (2021).10.1002/stem.3363 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
