Toxicological and Teratogenic Effect of Various Food Additives: An Updated Review
- PMID: 35782077
- PMCID: PMC9249520
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6829409
Toxicological and Teratogenic Effect of Various Food Additives: An Updated Review
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Toxicological and Teratogenic Effect of Various Food Additives: An Updated Review.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9792751. doi: 10.1155/2024/9792751. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38230185 Free PMC article.
Abstract
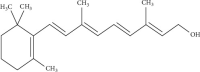
Scientific evidence is mounting that synthetic chemicals used as food additives may have harmful impacts on health. Food additives are chemicals that are added to food to keep it from spoiling, as well as to improve its colour and taste. Some are linked to negative health impacts, while others are healthy and can be ingested with little danger. According to several studies, health issues such as asthma, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), heart difficulties, cancer, obesity, and others are caused by harmful additives and preservatives. Some food additives may interfere with hormones and influences growth and development. It is one of the reasons why so many children are overweight. Children are more likely than adults to be exposed to these types of dietary intakes. Several food additives are used by women during pregnancy and breast feeding that are not fully safe. We must take specific precaution to avoid consuming dangerous compounds before they begin to wreak havoc on our health. This study is intended to understand how the preservatives induce different health problem in the body once it is consumed. This review focuses on some specific food additives such as sodium benzoate, aspartame, tartrazine, carrageenan, and potassium benzoate, as well as vitamin A. Long-term use of food treated with the above-mentioned food preservatives resulted in teratogenicity and other allergens, according to the study. Other health issues can be avoided in the future by using natural food additives derived from plants and other natural sources.
Copyright © 2022 Saseendran Sambu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vaclavik V. A., Christian E. W. Essentials of food science . Vol. 42. New York, Springer; 2008.
-
- Tantibanchachai C. Retinoids as teratogens . Embryo Project Encyclopedia; 2014.
-
- Winter R. A. Consumer’s Dictionary of Food Additives . Vol. 112. New York: Three River Press; 1994.
-
- Smoley C. K. In Everything Added to Food in the United States, US Food and Drug Administration . Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, Inc.; 1993.
-
- Inetianbor J. E., Yakubu J. M., Ezeonu S. C. Effects of food additives and preservatives on man-a review. Asian Journal of Science and Technology . 2015;6(2):1118–1135.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources