Microsporidia, a Highly Adaptive Organism and Its Host Expansion to Humans
- PMID: 35782144
- PMCID: PMC9245026
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.924007
Microsporidia, a Highly Adaptive Organism and Its Host Expansion to Humans
Abstract
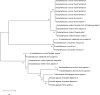
Emerging infectious disease has become the center of attention since the outbreak of COVID-19. For the coronavirus, bats are suspected to be the origin of the pandemic. Consequently, the spotlight has fallen on zoonotic diseases, and the focus now expands to organisms other than viruses. Microsporidia is a single-cell organism that can infect a wide range of hosts such as insects, mammals, and humans. Its pathogenicity differs among species, and host immunological status plays an important role in infectivity and disease severity. Disseminated disease from microsporidiosis can be fatal, especially among patients with a defective immune system. Recently, there were two Trachipleistophora hominis, a microsporidia species which can survive in insects, case reports in Thailand, one patient had disseminated microsporidiosis. This review gathered data of disseminated microsporidiosis and T. hominis infections in humans covering the biological and clinical aspects. There was a total of 22 cases of disseminated microsporidiosis reports worldwide. Ten microsporidia species were identified. Maximum likelihood tree results showed some possible correlations with zoonotic transmissions. For T. hominis, there are currently eight case reports in humans, seven of which had Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection. It is observed that risks are higher for the immunocompromised to acquire such infections, however, future studies should look into the entire life cycle, to identify the route of transmission and establish preventive measures, especially among the high-risk groups.
Keywords: Trachipleistophora hominis; disseminated microsporidiosis; microsporidia; opportunistic infection; zoonosis.
Copyright © 2022 Seatamanoch, Kongdachalert, Sunantaraporn, Siriyasatien and Brownell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson N. W., Muehlenbachs A., Arif S., Bruminhent J., Deziel P. J., Razonable R. R., et al. . (2019). A Fatal Case of Disseminated Microsporidiosis Due to Anncaliia Algerae in a Renal and Pancreas Allograft Recipient. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 6 (7), ofz285. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofz285 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becnel J. J., Andreadis T. G. (2014). “Microsporidia in Insects,” in Microsporidia. (USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.) 521–570.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

