circRNA circ_0055724 Inhibits Trophoblastic Cell Line HTR-8/SVneo's Invasive and Migratory Abilities via the miR-136/N-Cadherin Axis
- PMID: 35783018
- PMCID: PMC9242821
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9390731
circRNA circ_0055724 Inhibits Trophoblastic Cell Line HTR-8/SVneo's Invasive and Migratory Abilities via the miR-136/N-Cadherin Axis
Abstract
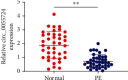
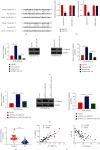
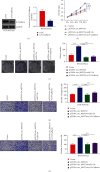
Preeclampsia (PE) is one of the major causes of morbidity and mortality in pregnancy. According to recent research, circular RNAs (circRNA) may act as sponges for microRNAs (miRNAs) and modulate gene expression. Low expression of hsa_circ_0055724 (circ_0055724) in PE tissues was recently reported in literatures. However, its mechanism and function have not been reported. Therefore, we were committed to investigating the role and mechanism of circ_0055724 in PE. Our study first verified the low expression of circ_0055724 in PE tissues. Overexpression or knockdown of circ_0055724 enhances/weakens the trophoblast cell survival, migration, and invasion. Furthermore, CircInteractome predicted the binding sites of circ_0055724 and miR-136, while Starbase predicted miR-136 targeted N-cadherin. Luciferase reporter gene assay confirmed that circ_0055724 directly interacts with miR-136 and miR-136 directly interacts with N-cadherin. More results indicated that high expression of miR-136 and low expression of N-cadherin appeared in PE. Increased expression of circ_0055724 resulted in decreased miR-136 but increased N-cadherin expression. Hence, circ_0055724 and N-cadherin were positively correlated, while circ_0055724 and miR-136 had a negative correlation. In terms of mechanism, circ_0055724 may induce the expression of N-cadherin and regulate the proliferation, migration, and invasion of trophoblast cells through decreasing miR-136, which can be a promising biomarker for early diagnosis and prognosis of patients with PE.
Copyright © 2022 Xiaohong Xu and Hong Teng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circ_0085296 suppresses trophoblast cell proliferation, invasion, and migration via modulating miR-144/E-cadherin axis.Placenta. 2020 Aug;97:18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2020.06.002. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Placenta. 2020. PMID: 32792057
-
Hsa_circ_0001326 inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of trophoblast cells via miR-145-5p/TGFB2 axis.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2023 May;89(5):e13682. doi: 10.1111/aji.13682. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36670490
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0026552 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of trophoblast cells via the miR‑331‑3p/TGF‑βR1 axis in pre‑eclampsia.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Nov;24(5):798. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12438. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34523694 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of circRNA hsa_circ_0008726 in Pre-eclampsia Inhibits Trophoblast Migration, Invasion, and EMT by Regulating miR-345-3p/RYBP Axis.Reprod Sci. 2022 Oct;29(10):2829-2841. doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00804-y. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Reprod Sci. 2022. PMID: 34845670 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0081343 promotes trophoblast cell migration and invasion and inhibits trophoblast apoptosis by regulating miR-210-5p/DLX3 axis.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021 Aug 9;19(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00795-0. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34365964 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Circ_0003314 Combines with the miR-26b-5p/IL1RAP Axis to Inhibit HTR-8/SVneo Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Tube Formation and Promote Apoptosis.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Jan;197(1):443-458. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-05011-4. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39141177
-
Unveiling the Network regulatory mechanism of ncRNAs on the Ferroptosis Pathway: Implications for Preeclampsia.Int J Womens Health. 2024 Sep 30;16:1633-1651. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S485653. eCollection 2024. Int J Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 39372667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current understanding of circular RNAs in preeclampsia.Hypertens Res. 2024 Jun;47(6):1607-1619. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01675-x. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 38605141 Review.
References
-
- Macedo T. C. C., Montagna E., Trevisan C. M., et al. Prevalence of preeclampsia and eclampsia in adolescent pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 291,247 adolescents worldwide since 1969. European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology . 2020;248:177–186. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.03.043. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

