Vestibular Hair Cells Require CAMSAP3, a Microtubule Minus-End Regulator, for Formation of Normal Kinocilia
- PMID: 35783105
- PMCID: PMC9247359
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.876805
Vestibular Hair Cells Require CAMSAP3, a Microtubule Minus-End Regulator, for Formation of Normal Kinocilia
Abstract
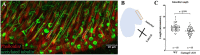
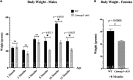
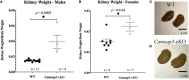
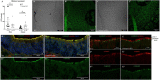
Kinocilia are exceptionally long primary sensory cilia located on vestibular hair cells, which are essential for transmitting key signals that contribute to mammalian balance and overall vestibular system function. Kinocilia have a "9+2" microtubule (MT) configuration with nine doublet MTs surrounding two central singlet MTs. This is uncommon as most mammalian primary sensory cilia have a "9+0" configuration, in which the central MT pair is absent. It has yet to be determined what the function of the central MT pair is in kinocilia. Calmodulin-regulated spectrin-associated protein 3 (CAMSAP3) regulates the minus end of MTs and is essential for forming the central MT pair in motile cilia, which have the "9+2" configuration. To explore the role of the central MT pair in kinocilia, we created a conditional knockout model (cKO), Camsap3-cKO, which intended to eliminate CAMSAP3 in limited organs including the inner ear, olfactory bulb, and kidneys. Immunofluorescent staining of vestibular organs demonstrated that CAMSAP3 proteins were significantly reduced in Camsap3-cKO mice and that aged Camsap3-cKO mice had significantly shorter kinocilia than their wildtype littermates. Transmission electron microscopy showed that aged Camsap3-cKO mice were in fact missing that the central MT pair in kinocilia more often than their wildtype counterparts. In the examination of behavior, wildtype and Camsap3-cKO mice performed equally well on a swim assessment, right-reflex test, and evaluation of balance on a rotarod. However, Camsap3-cKO mice showed slightly altered gaits including reduced maximal rate of change of paw area and a smaller paw area in contact with the surface. Although Camsap3-cKO mice had no differences in olfaction from their wildtype counterparts, Camsap3-cKO mice did have kidney dysfunction that deteriorated their health. Thus, CAMSAP3 is important for establishing and/or maintaining the normal structure of kinocilia and kidney function but is not essential for normal olfaction. Our data supports our hypothesis that CAMSAP3 is critical for construction of the central MT pair in kinocilia, and that the central MT pair may be important for building long and stable axonemes in these kinocilia. Whether shorter kinocilia might lead to abnormal vestibular function and altered gaits in older Camsap3-cKO mice requires further investigation.
Keywords: CAMSAP3; gait; kidney dysfunction; kinocilia; vestibular function; “9+2” configuration.
Copyright © 2022 O’Donnell and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CAMSAP3 facilitates basal body polarity and the formation of the central pair of microtubules in motile cilia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 16;117(24):13571-13579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1907335117. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32482850 Free PMC article.
-
Rab11a Regulates the Development of Cilia and Establishment of Planar Cell Polarity in Mammalian Vestibular Hair Cells.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Nov 19;14:762916. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.762916. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34867187 Free PMC article.
-
Tracheal motile cilia in mice require CAMSAP3 for the formation of central microtubule pair and coordinated beating.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Oct 1;32(20):ar12. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-06-0303. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34319756 Free PMC article.
-
Cilia in the developing zebrafish ear.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Feb 17;375(1792):20190163. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0163. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31884918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Kinocilia of Cochlear Hair Cells: Structures, Functions, and Diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 5;9:715037. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.715037. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34422834 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berryman E. R., Harris R. L., Moalli M., Bagi C. M. (2009). Digigait quantitation of gait dynamics in rat rheumatoid arthritis model. J. Musculoskelet Neuronal. Interact. 9 89–98. - PubMed
-
- Brings V. E., Payne M. A., Gereau R. W. (2021). Paw placement during walking is altered by analgesic doses of opioids and post-surgical injury in mice. bioRxiv 10.1101/2021.12.15.4728182012 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

