Identification of Hypoxia-Related Subtypes, Establishment of Prognostic Models, and Characteristics of Tumor Microenvironment Infiltration in Colon Cancer
- PMID: 35783281
- PMCID: PMC9247151
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.919389
Identification of Hypoxia-Related Subtypes, Establishment of Prognostic Models, and Characteristics of Tumor Microenvironment Infiltration in Colon Cancer
Abstract
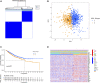
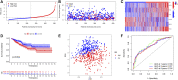
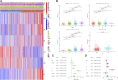
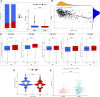
Background: Immunotherapy is a treatment that can significantly improve the prognosis of patients with colon cancer, but the response to immunotherapy is different in patients with colon cancer because of the heterogeneity of colon carcinoma and the complex nature of the tumor microenvironment (TME). In the precision therapy mode, finding predictive biomarkers that can accurately identify immunotherapy-sensitive types of colon cancer is essential. Hypoxia plays an important role in tumor proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis, energy metabolism, and chemotherapy and immunotherapy resistance. Thus, understanding the mechanism of hypoxia-related genes (HRGs) in colon cancer progression and constructing hypoxia-related signatures will help enrich our treatment strategies and improve patient prognosis. Methods: We obtained the gene expression data and corresponding clinical information of 1,025 colon carcinoma patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases, respectively. We identified two distinct hypoxia subtypes (subtype A and subtype B) according to unsupervised clustering analysis and assessed the clinical parameters, prognosis, and TME cell-infiltrating characteristics of patients in the two subtypes. We identified 1,132 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the two hypoxia subtypes, and all patients were randomly divided into the training group (n = 513) and testing groups (n = 512). Following univariate Cox regression with DEGs, we construct the prognostic model (HRG-score) including six genes (S1PR3, ETV5, CD36, FOXC1, CXCL10, and MMP12) through the LASSO-multivariate cox method in the training group. We comprehensively evaluated the sensitivity and applicability of the HRG-score model from the training group and the testing group, respectively. We explored the correlation between HRG-score and clinical parameters, tumor microenvironment, cancer stem cells (CSCs), and MMR status. In order to evaluate the value of the risk model in clinical application, we further analyzed the sensitivity of chemotherapeutics and immunotherapy between the low-risk group and high-risk group and constructed a nomogram for improving the clinical application of the HRG-score. Result: Subtype A was significantly enriched in metabolism-related pathways, and subtype B was significantly enriched in immune activation and several tumor-associated pathways. The level of immune cell infiltration and immune checkpoint-related genes, stromal score, estimate score, and immune dysfunction and exclusion (TIDE) prediction score was significantly different in subtype A and subtype B. The level of immune checkpoint-related genes and TIDE score was significantly lower in subtype A than that in subtype B, indicating that subtype A might benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors. Finally, an HRG-score signature for predicting prognosis was constructed through the training group, and the predictive capability was validated through the testing group. The survival analysis and correlation analysis of clinical parameters revealed that the prognosis of patients in the high-risk group was significantly worse than that in the low-risk group. There were also significant differences in immune status, mismatch repair status (MMR), and cancer stem cell index (CSC), between the two risk groups. The correlation analysis of risk scores with IC50 and IPS showed that patients in the low-risk group had a higher benefit from chemotherapy and immunotherapy than those in the high-risk group, and the external validation IMvigor210 demonstrated that patients with low risk were more sensitive to immunotherapy. Conclusion: We identified two novel molecular subgroups based on HRGs and constructed an HRG-score model consisting of six genes, which can help us to better understand the mechanisms of hypoxia-related genes in the progression of colon cancer and identify patients susceptible to chemotherapy or immunotherapy, so as to achieve precision therapy for colon cancer.
Keywords: HRG-score; colon cancer; hypoxia-related genes; immune checkpoint blockade; immunotherapy; molecular subtype; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Tang, Ma, Wei, Hu, Zhao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of cuproptosis-related subtypes, construction of a prognosis model, and tumor microenvironment landscape in gastric cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 21;13:1056932. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1056932. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36479114 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of angiogenesis-related subtypes, the development of a prognosis model, and features of tumor microenvironment in colon cancer.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2024 Feb;71(1):45-60. doi: 10.1002/bab.2520. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37881150
-
Identification and validation of a dysregulated TME-related gene signature for predicting prognosis, and immunological properties in bladder cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 27;14:1213947. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1213947. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37965307 Free PMC article.
-
Constructing and validating a risk model based on neutrophil-related genes for evaluating prognosis and guiding immunotherapy in colon cancer.J Gene Med. 2024 Apr;26(4):e3684. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3684. J Gene Med. 2024. PMID: 38618694 Review.
-
A novel necroptosis-related gene index for predicting prognosis and a cold tumor immune microenvironment in stomach adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 27;13:968165. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.968165. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389725 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis and systematic review of factors predicting conversion to radical nephrectomy following robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy in renal cancer patients.J Robot Surg. 2024 Oct 24;18(1):377. doi: 10.1007/s11701-024-02147-7. J Robot Surg. 2024. PMID: 39443332
-
Predictive biomarkers of colon cancer immunotherapy: Present and future.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 22;13:1032314. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1032314. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36483562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ETV5 reduces androgen receptor expression and induces neural stem-like properties during neuroendocrine prostate cancer development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Mar 25;122(12):e2420313122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2420313122. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40117308
-
Radiomics signature for dynamic changes of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and macrophages in cervical cancer during chemoradiotherapy.Cancer Imaging. 2024 Apr 23;24(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00680-0. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38654284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bekaii-Saab T. S., Ou F.-S., Ahn D. H., Boland P. M., Ciombor K. K., Heying E. N., et al. (2019). Regorafenib Dose-Optimisation in Patients with Refractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (ReDOS): a Randomised, Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 2 Study. Lancet. Oncol. 20 (8), 1070–1082. 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30272-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

