Case Report: Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia in a Chinese Child Treated With Growth Hormone
- PMID: 35783312
- PMCID: PMC9249018
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.921323
Case Report: Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia in a Chinese Child Treated With Growth Hormone
Abstract
Background: Glycogen storage disease type Ia is a rare metabolic disorder that leads to excessive glycogen and fat accumulation in organs, characterized by hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, lactic acidemia, hyperlipidemia, hyperuricemia, puberty delay, and growth retardation. Here, we report on a patient with glycogen storage disease type Ia treated with growth hormone.
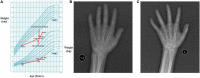
Case presentation: A 10-year-old boy had growth retardation for 6 years, and was admitted to clarify the cause of his short stature. We found that his bone age was 5.5 years, significantly lower than his physical age, while his serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 were 23.30 and 1620.0 ng/mL, respectively, both lower than normal. His medical history revealed that he had suffered from steatohepatitis, hyperlipidemia, and hypoglycemia since he was 11 months of age. Whole exome sequencing (WES) showed compound heterozygous mutations in exons 2 and 5 of the glucose-6-phosphatase (G6PC) gene on chromosome 17: c.G248A (p.R83H) and c.G648T (p.L216L). The patient was finally diagnosed with GSD Ia. After growth hormone (GH) treatment and corn starch therapy for 14 months, his height significantly increased (by 13 cm). The serum IGF-1 level increased to the normal range but his lipid levels and liver function did not significantly increase.
Conclusion: We describe a young patient with a compound heterozygous G6PC variant in a Chinese family; his height increased significantly after growth hormone and corn starch interventions. This case emphasizes that WES is essential for early diagnosis, and that growth hormone treatment may increase the height of patients with GSD Ia safely.
Keywords: G6PC gene; GSD Ia; compound heterozygous variant; growth hormone treatment; growth retardation.
Copyright © 2022 Wu, Guo, Fu, Du and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

