Artificial intelligence and IoT based prediction of Covid-19 using chest X-ray images
- PMID: 35783463
- PMCID: PMC9233885
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smhl.2022.100299
Artificial intelligence and IoT based prediction of Covid-19 using chest X-ray images
Abstract
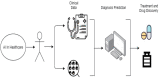
Coronavirus illness (COVID-19), discovered in late 2019, has spread rapidly worldwide, resulting in significant mortality. This study analyzed the performance of studies that employed machines and DL on chest X-ray pictures and CT scans for COVID-19 diagnosis. ML approaches on CT and X-ray images aided incorrectly in identifying COVID-19. The fast spread of COVID-19 worldwide and the growing number of deaths necessitates an immediate response from all sectors. Authorities will be able to deal with the effects more efficiently if such illnesses can be predicted in the future. Furthermore, it is crucial to maintain track of the number of infected persons through regular check-ups, and it is frequently required to confine affected people and implement medical treatments. In addition, various additional elements, such as environmental influences and commonalities among the most afflicted places, should be considered to slow the spread of COVID-19, and precautions should be taken. AI-based approaches for the prediction and diagnosis of COVID-19 were suggested in this paper. This Review Article discusses current advances in AI technology and its biological applications, particularly the coronavirus.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Corona detection; Corona virus; Covid-19; Deep learning.
© 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
"Fast deep learning computer-aided diagnosis of COVID-19 based on digital chest x-ray images".Appl Intell (Dordr). 2021;51(5):2890-2907. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-02076-6. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Appl Intell (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 34764573 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Pneumonia Diagnosis Using a Simple 2D Deep Learning Framework With a Single Chest CT Image: Model Development and Validation.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Jun 29;22(6):e19569. doi: 10.2196/19569. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32568730 Free PMC article.
-
A narrative review on characterization of acute respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19-infected lungs using artificial intelligence.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Mar;130:104210. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104210. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33550068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI-Empowered Computational Examination of Chest Imaging for COVID-19 Treatment: A Review.Front Artif Intell. 2021 Jul 21;4:612914. doi: 10.3389/frai.2021.612914. eCollection 2021. Front Artif Intell. 2021. PMID: 34368756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 image classification using deep learning: Advances, challenges and opportunities.Comput Biol Med. 2022 May;144:105350. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105350. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35305501 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Large-Scale IoT-Based Scheme for Real-Time Prediction of Infectious Disease Symptoms.Mob Netw Appl. 2023 Feb 2:1-19. doi: 10.1007/s11036-023-02111-z. Online ahead of print. Mob Netw Appl. 2023. PMID: 40479340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ardakani A.A., Kanafi A.R., Acharya U.R., Khadem N., Mohammadi A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2020;121 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103795. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aswathy S.U., Jarin T., Mathews R., Nair L.M., Rroan M. CAD systems for automatic detection and classification of COVID-19 in nano CT lung image by using machine learning technique. International Journal of Pharmacology Research. 2020;12:1865–1870. doi: 10.31838/ijpr/2020.12.02.247. - DOI
Further reading
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources