Ketone Bodies Improve Human CD8+ Cytotoxic T-Cell Immune Response During COVID-19 Infection
- PMID: 35783654
- PMCID: PMC9243504
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.923502
Ketone Bodies Improve Human CD8+ Cytotoxic T-Cell Immune Response During COVID-19 Infection
Abstract
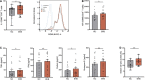
Severe COVID-19 is characterized by profound CD8+ T-cell dysfunction, which cannot be specifically treated to date. We here investigate whether metabolic CD8+ T-cell reprogramming by ketone bodies could be a promising strategy to overcome the immunoparalysis in COVID-19 patients. This approach was triggered by our recent pioneering study, which has provided evidence that CD8+ T-cell capacity in healthy subjects could be significantly empowered by a Ketogenic Diet. These improvements were achieved by immunometabolic rewiring toward oxidative phosphorylation. We here report similar strengthening of CD8+ T cells obtained from severely diseased COVID-19 patients: Flow cytometry and ELISA revealed elevated cytokine expression and secretion (up to + 24%) upon ketone treatment and enhanced cell lysis capacity (+ 21%). Metabolic analyses using Seahorse technology revealed upregulated mitochondrial respiratory chain activity (+ 25%), enabling both superior energy supply (+ 44%) and higher mitochondrial reactive oxygen species signaling. These beneficial effects of ketones might represent evolutionary conserved mechanisms to strengthen human immunity. Our findings pave the road for metabolic treatment studies in COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Ketogenic Diet (KD); SARS-CoV-2; T-cell immunometabolism; cytotoxic T cell; metabolic therapy; nutritional immunology.
Copyright © 2022 Hirschberger, Gellert, Effinger, Muenchhoff, Herrmann, Briegel, Zwißler and Kreth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Very-low-carbohydrate diet enhances human T-cell immunity through immunometabolic reprogramming.EMBO Mol Med. 2021 Aug 9;13(8):e14323. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202114323. Epub 2021 Jun 21. EMBO Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34151532 Free PMC article.
-
Ketogenic Diet and Ketone Bodies as Clinical Support for the Treatment of SARS-CoV-2-Review of the Evidence.Viruses. 2023 May 27;15(6):1262. doi: 10.3390/v15061262. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37376562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: Proposing a Ketone-Based Metabolic Therapy as a Treatment to Blunt the Cytokine Storm.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Sep 9;2020:6401341. doi: 10.1155/2020/6401341. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33014275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Defects of Peripheral T Cells in COVID-19 Patients.J Immunol. 2021 Jun 15;206(12):2900-2908. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100068. Epub 2021 May 28. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34049969
-
Expression of NKG2A inhibitory receptor on cytotoxic lymphocytes as an indicator of severity in Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients.Egypt J Immunol. 2021 Jul;28(3):157-167. Egypt J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34453787
Cited by
-
Diabetes Mellitus, Energy Metabolism, and COVID-19.Endocr Rev. 2024 Mar 4;45(2):281-308. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnad032. Endocr Rev. 2024. PMID: 37934800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ketogenic diet in treating sepsis-related acquired weakness: is it friend or foe?Front Nutr. 2024 Nov 28;11:1484856. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1484856. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39668897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered immunometabolic response to fasting in humans living with obesity.iScience. 2025 Jun 11;28(7):112872. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112872. eCollection 2025 Jul 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40662191 Free PMC article.
-
[Immunomodulation by nutritional intervention in critically ill patients].Anaesthesiologie. 2023 Apr;72(4):229-244. doi: 10.1007/s00101-023-01258-4. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Anaesthesiologie. 2023. PMID: 36797533 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
A ketogenic diet enhances fluconazole efficacy in murine models of systemic fungal infection.mBio. 2024 May 8;15(5):e0064924. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00649-24. Epub 2024 Apr 15. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38619236 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

