The Metacognitive and Neurocognitive Signatures of Test Methods in Academic Listening
- PMID: 35783744
- PMCID: PMC9245920
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.930075
The Metacognitive and Neurocognitive Signatures of Test Methods in Academic Listening
Abstract
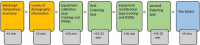
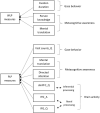
This study aims to investigate whether and how test takers' academic listening test performance is predicted by their metacognitive and neurocognitive process under different test methods conditions. Eighty test takers completed two tests consisting of while-listening performance (WLP) and post-listening performance (PLP) test methods. Their metacognitive awareness was measured by the Metacognitive Awareness Listening Questionnaire (MALQ), and gaze behavior and brain activation were measured by an eye-tracker and functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), respectively. The results of automatic linear modeling indicated that WLP and PLP test performances were predicted by different factors. The predictors of WLP test performance included two metacognitive awareness measures (i.e., person knowledge and mental translation) and fixation duration. In contrast, the predictors of the PLP performance comprised two metacognitive awareness measures (i.e., mental translation and directed attention), visit counts, and importantly, three brain activity measures: the dmPFC measure in the answering phase, IFG measure in the listening phase, and IFG measure in the answering phase. Implications of these findings for language assessment are discussed.
Keywords: eye-tracking; functional near-infrared spectroscopy; listening comprehension assessment; metacognitive awareness; non-invasive neurotechnologies.
Copyright © 2022 Zhai and Aryadoust.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring the relationship between metacognitive awareness and Chinese EFL learners' listening skills.Front Psychol. 2023 May 2;14:1148610. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1148610. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37205072 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediating Effect of Listening Metacognitive Awareness between Test-Taking Motivation and Listening Test Score: An Expectancy-Value Theory Approach.Front Psychol. 2017 Dec 22;8:2201. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02201. eCollection 2017. Front Psychol. 2017. PMID: 29312063 Free PMC article.
-
EFL Listening, Metacognitive Awareness, and Motivation: The Magic of L1-Mediated Metacognitive Intervention.J Psycholinguist Res. 2023 Apr;52(2):477-495. doi: 10.1007/s10936-022-09895-3. Epub 2022 Jun 22. J Psycholinguist Res. 2023. PMID: 35732876
-
Modeling the relationships between EFL learners' construct-relevant and -irrelevant strategies in listening test performance.Acta Psychol (Amst). 2024 Nov;251:104623. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2024.104623. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2024. PMID: 39647450
-
[Awareness of deficits and anosognosia in Alzheimer's disease].Encephale. 2004 Nov-Dec;30(6):570-7. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95472-3. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15738860 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Cognitive diagnostic assessment of EFL learners' listening barriers through incorrect responses.Front Psychol. 2023 Aug 17;14:1126106. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1126106. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37663352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alderson J. C., Bachman L. F. (2001). “Series editors’ preface,” in Assessing Listening, ed. Buck G. (Cambridge University Press; ).
-
- Aryadoust V. (2012). Differential item functioning in while-listening performance tests: the case of the international english language testing system (IELTS) listening module. Int. J. List. 26 40–60. 10.1080/10904018.2012.639649 - DOI
-
- Aryadoust V. (2015). Fitting a mixture rasch model to english as a foreign language listening tests: the role of cognitive and background variables in explaining latent differential item functioning. Int. J. Test. 15 216–238. 10.1080/15305058.2015.1004409 - DOI
-
- Aryadoust V. (2019a). An integrated cognitive theory of comprehension. Int. J. List. 33 71–100. 10.1080/10904018.2017.1397519 - DOI
-
- Aryadoust V. (2019b). Dynamics of item reading and answer changing in two hearings in a computerized while-listening performance test: an eye-tracking study. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 33 510–537. 10.1080/09588221.2019.1574267 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

