Genome-Wide Characterization of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Genes in Daucus carota: Novel Insights Into Structure, Expression, and Binding Interaction With Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Under Abiotic Stress Condition
- PMID: 35783965
- PMCID: PMC9246500
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.870241
Genome-Wide Characterization of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Genes in Daucus carota: Novel Insights Into Structure, Expression, and Binding Interaction With Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Under Abiotic Stress Condition
Abstract
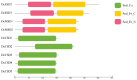
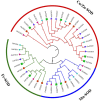
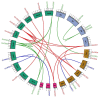
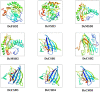
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) proteins are important antioxidant enzymes that help plants to grow, develop, and respond to a variety of abiotic stressors. SOD gene family has been identified in a number of plant species but not yet in Daucus carota. A total of 9 DcSOD genes, comprising 2 FeSODs, 2 MnSODs, and 5 Cu/ZnSODs, are identified in the complete genome of D. carota, which are dispersed in five out of nine chromosomes. Based on phylogenetic analysis, SOD proteins from D. carota were categorized into two main classes (Cu/ZnSODs and MnFeSODs). It was predicted that members of the same subgroups have the same subcellular location. The phylogenetic analysis was further validated by sequence motifs, exon-intron structure, and 3D protein structures, with each subgroup having a similar gene and protein structure. Cis-regulatory elements responsive to abiotic stresses were identified in the promoter region, which may contribute to their differential expression. Based on RNA-seq data, tissue-specific expression revealed that DcCSD2 had higher expression in both xylem and phloem. Moreover, DcCSD2 was differentially expressed in dark stress. All SOD genes were subjected to qPCR analysis after cold, heat, salt, or drought stress imposition. SODs are antioxidants and play a critical role in removing reactive oxygen species (ROS), including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). DcSODs were docked with H2O2 to evaluate their binding. The findings of this study will serve as a basis for further functional insights into the DcSOD gene family.
Keywords: abiotic stress; carrot; comparative modeling; expression pattern; molecular docking; phylogeny; reactive oxygen species; superoxide dismutase.
Copyright © 2022 Zameer, Fatima, Azeem, ALgwaiz, Sadaqat, Rasheed, Batool, Shah, Zaynab, Shah, Attia, AlKahtani and Fiaz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis of the superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Zostera marina and expression profile analysis under temperature stress.PeerJ. 2020 May 5;8:e9063. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9063. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32411532 Free PMC article.
-
In silico identification and expression analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Medicago truncatula.3 Biotech. 2018 Aug;8(8):348. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1373-1. Epub 2018 Jul 30. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 30073133 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of abiotic-stress responsive SOD (superoxide dismutase) gene family in Brassica juncea and B. rapa.BMC Genomics. 2019 Mar 19;20(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5593-5. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30890148 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) genes in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.).3 Biotech. 2018 Dec;8(12):486. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1502-x. Epub 2018 Nov 16. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 30498660 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression Characteristics and Regulation Mechanisms of Superoxide Dismutase and Its Physiological Roles in Plants under Stress.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2016 May;81(5):465-80. doi: 10.1134/S0006297916050047. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2016. PMID: 27297897 Review.
Cited by
-
Leaf litter from Cynanchum auriculatum Royle ex Wight leads to root rot outbreaks by Fusarium solani, hindering continuous cropping.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2024 May 14;100(6):fiae068. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiae068. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2024. PMID: 38684466 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Cadmium on Plants in Terms of the Response of Gene Expression Level and Activity.Plants (Basel). 2023 Apr 30;12(9):1848. doi: 10.3390/plants12091848. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37176906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exogenous Cytokinin 4PU-30 Modulates the Response of Wheat and Einkorn Seedlings to Ultraviolet B Radiation.Plants (Basel). 2024 May 17;13(10):1401. doi: 10.3390/plants13101401. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794471 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of Micro/Nanoplastics Combined with Graphene Oxide on Lactuca sativa Seeds: Insights into Seedling Growth, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidant Gene Expression.Plants (Basel). 2024 Dec 11;13(24):3466. doi: 10.3390/plants13243466. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771164 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of two-component system (TCS) genes in Brassica oleracea in response to shade stress.Front Genet. 2023 May 30;14:1142544. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1142544. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37323660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C., Chen H., He Y., Xia R. (2018). TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various biological data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. bioRxiv. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

