Grain Transcriptome Dynamics Induced by Heat in Commercial and Traditional Bread Wheat Genotypes
- PMID: 35783979
- PMCID: PMC9248373
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.842599
Grain Transcriptome Dynamics Induced by Heat in Commercial and Traditional Bread Wheat Genotypes
Abstract
High temperature (HT) events have negative impact on wheat grains yield and quality. Transcriptome profiles of wheat developing grains of commercial genotypes (Antequera and Bancal) and landraces (Ardito and Magueija) submitted to heatwave-like treatments during grain filling were evaluated. Landraces showed significantly more differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and presented more similar responses than commercial genotypes. DEGs were more associated with transcription and RNA and protein synthesis in Antequera and with metabolism alterations in Bancal and landraces. Landraces upregulated genes encoding proteins already described as HT responsive, like heat shock proteins and cupins. Apart from the genes encoding HSP, two other genes were upregulated in all genotypes, one encoding for Adenylate kinase, essential for the cellular homeostasis, and the other for ferritin, recently related with increased tolerance to several abiotic stress in Arabidopsis. Moreover, a NAC transcription factor involved in plant development, known to be a negative regulator of starch synthesis and grain yield, was found to be upregulated in both commercial varieties and downregulated in Magueija landrace. The detected diversity of molecular processes involved in heat response of commercial and traditional genotypes contribute to understand the importance of genetic diversity and relevant pathways to cope with these extreme events.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; bread wheat; commercial varieties; grain transcriptome; heatwave; landraces.
Copyright © 2022 Tomás, Viegas and Silva.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
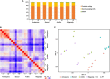
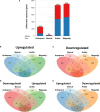




References
-
- Altenbach S. B., Kothari K. M. (2004). Transcript profiles of genes expressed in endosperm tissue are altered by high temperature during wheat grain development. J. Cereal Sci. 40 115–126. 10.1016/j.jcs.2004.05.004 - DOI
-
- Andrews S., Krueger F., Segonds-Pichon A., Biggins L., Krueger C., Wingett S., et al. (2010). FastQC: a Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Babraham: Babraham Institute.
-
- ANPOC, INIAV, IpBeja, Ceres, Germen, and Cerealis (2014). Lista de Variedade Recomendadas Sementeiras Trigo Mole. Lisboa.
-
- Asseng S., Ewert F., Martre P., Rötter R. P., Lobell D. B., Cammarano D., et al. (2014). Rising temperatures reduce global wheat production. Nat. Clim. Change 5 143–147. 10.1038/nclimate2470 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

