A Prospectively Validated Nomogram for Predicting the Risk of PHQ-9 Score ≥15 in Patients With Erectile Dysfunction: A Multi-Center Study
- PMID: 35784263
- PMCID: PMC9247334
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.836898
A Prospectively Validated Nomogram for Predicting the Risk of PHQ-9 Score ≥15 in Patients With Erectile Dysfunction: A Multi-Center Study
Abstract
Background: Although erectile dysfunction (ED) often occurs simultaneously with depression, not all patients with ED suffer major depression (MD), with a PHQ-9 score ≥15 indicating MD. Because the PHQ-9 questionnaire includes phrases such as "I think I am a loser" and "I want to commit suicide," the psychological burdens of ED patients are likely to increase inevitably after using the PHQ-9, which, in turn, may affect ED therapeutic effects. Accordingly, we endeavored to develop a nomogram to predict individual risk of PHQ-9 score ≥15 in these patients.
Methods: The data of 1,142 patients with ED diagnosed in Xijing Hospital and Northwest Women and Children's Hospital from January 2017 to May 2020 were analyzed. While the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator regression was employed to screen PHQ-9 score ≥15 related risk factors, multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to verify these factors and construct the nomogram. The training cohort and an independent cohort that comprised 877 prospectively enrolled patients were used to demonstrate the efficacy of the nomogram.
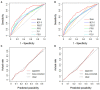
Results: The IIEF-5 score, PEDT score, physical pain score, frequent urination, and feeling of endless urination were found to be independent factors of PHQ-9 score ≥15 in patients with ED. The nomogram developed by these five factors showed good calibration and discrimination in internal and external validation, with a predictive accuracy of 0.757 and 0.722, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of the nomogram in the training cohort were 0.86 and 0.52, respectively. Besides, the sensitivity and specificity of the nomogram in the validation cohort were 0.73 and 0.62, respectively. Moreover, based on the nomogram, the sample was divided into low-risk and high-risk groups.
Conclusion: This study established a nomogram to predict individual risk of PHQ-9 score ≥15 in patients with ED. It is deemed that the nomogram may be employed initially to avoid those with a low risk of MD completing questionnaires unnecessarily.
Keywords: erectile dysfunction; major depression; nomogram; prognostic factor; risk factor.
Copyright © 2022 Zheng, Gao, Hou, Hou, Feng, Jannini, Wei, Zheng, Zhang, Dun, Zhang, Wang, Meng, Jannini and Yuan.
Conflict of interest statement
EJ has been a consultant and/or paid speaker for Bayer, Ibsa, Lundbeck, Menarini, Otsuka, Pfizer, and Shionogi. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

