HBx Mediated Increase of DDX17 Contributes to HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumorigenesis
- PMID: 35784274
- PMCID: PMC9243429
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.871558
HBx Mediated Increase of DDX17 Contributes to HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumorigenesis
Abstract
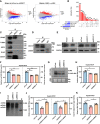
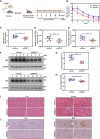
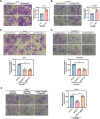
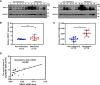
HBV is strongly associated with HCC development and DEAD-box RNA helicase 17 (DDX17) is a very important member of the DEAD box family that plays key roles in HCC development by promoting cancer metastasis. However, the important role of DDX17 in the pathogenesis of HBV-related HCC remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the role of DDX17 in the replication of HBV and the development of HBV-associated HCC. Based on data from the GEO database and HBV-infected cells, we found that DDX17 was upregulated by the HBV viral protein X (HBx). Mechanistically, increased DDX17 expression promoted HBV replication and transcription by upregulating ZWINT. Further study showed that DDX17 could promote HBx-mediated HCC metastasis. Finally, the promotive effect of DDX17 on HBV and HBV-related HCC was confirmed in vivo. In summary, the results revealed the novel role of DDX17 in the replication of HBV and the metastasis of HBV-associated HCC.
Keywords: DDX17; HBx; HCC; ZWINT; metastasis.
Copyright © 2022 Dong, Wen, He, Ren, Yu, Qin, Yang, Yang, Zhou, Zhang, Cheng and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNA Helicase DDX17 Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Blocking Viral Pregenomic RNA Encapsidation.J Virol. 2021 Sep 9;95(19):e0044421. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00444-21. Epub 2021 Sep 9. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34287051 Free PMC article.
-
HBx mediated Increase of SIRT1 Contributes to HBV-related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumorigenesis.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Jul 9;17(12):1783-1794. doi: 10.7150/ijms.43491. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32714081 Free PMC article.
-
Helicases DDX5 and DDX17 promote heterogeneity in HBV transcription termination in infected human hepatocytes.J Hepatol. 2024 Oct;81(4):609-620. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.05.016. Epub 2024 May 22. J Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38782119
-
The Epigenetic Modulation of Cancer and Immune Pathways in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Influence of HBx and miRNA Dysregulation.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 29;12:661204. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.661204. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The oncogenic role of hepatitis B virus.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014;193:59-74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-38965-8_4. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24008293 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of hepatitis B virus non-structural protein HBx on HBV replication, interferon signaling, and hepatocarcinogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Dec 21;14:1322892. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1322892. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38188582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Insight into the Arising Role of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Future Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 12;24(8):7168. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087168. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DDX17-Mediated Upregulation of CXCL8 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via Co-activating β-catenin/NF-κB Complex.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jan 20;21(3):1342-1360. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.104165. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39897048 Free PMC article.
-
Established and Emerging Roles of DEAD/H-Box Helicases in Regulating Infection and Immunity.Immunol Rev. 2025 Jan;329(1):e13426. doi: 10.1111/imr.13426. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Immunol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39620586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic and immunological landscape of DDX17 in pan-cancer analysis: a comprehensive study.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 17;16(1):1132. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02955-9. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40526173 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

