Helios Expression Is Downregulated on CD8+ Treg in Two Mouse Models of Lupus During Disease Progression
- PMID: 35784310
- PMCID: PMC9244697
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.922958
Helios Expression Is Downregulated on CD8+ Treg in Two Mouse Models of Lupus During Disease Progression
Abstract
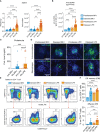
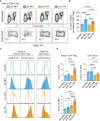
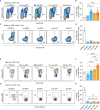
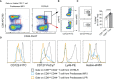
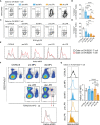
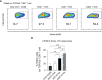
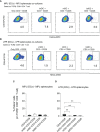
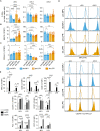
T-cell-mediated autoimmunity reflects an imbalance in this compartment that is not restored by tolerogenic immune cells, e.g., regulatory T cells or tolerogenic dendritic cells (tolDCs). Although studies into T-cell equilibrium have mainly focused on regulatory CD4+FoxP3+ T cells (CD4+ Tregs), recent findings on the lesser known CD8+ Tregs (CD44+CD122+Ly49+) have highlighted their non-redundant role in regulating lupus-like disease and their regulatory phenotype facilitated by the transcription factor Helios in mice and humans. However, there are still remaining questions about Helios regulation and dynamics in different autoimmune contexts. Here, we show the absence of CD8+ Tregs in two lupus-prone murine models: MRL/MPJ and MRL/lpr, in comparison with a non-prone mouse strain like C57BL/6. We observed that all MRL animals showed a dramatically reduced population of CD8+ Tregs and a greater Helios downregulation on diseased mice. Helios induction was detected preferentially on CD8+ T cells from OT-I mice co-cultured with tolDCs from C57BL/6 but not in MRL animals. Furthermore, the Helios profile was also altered in other relevant T-cell populations implicated in lupus, such as CD4+ Tregs, conventional CD4+, and double-negative T cells. Together, these findings could make Helios a versatile maker across the T-cell repertoire that is capable of differentiating lupus disease states.
Keywords: CD8+ Treg; Helios; autoimmunity; dendritic cells; lupus; tolerance; tolerogenic DC.
Copyright © 2022 París-Muñoz, Aizpurua and Barber.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Helios as a Potential Biomarker in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and New Therapies Based on Immunosuppressive Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 29;25(1):452. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010452. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helios Deficiency Predisposes the Differentiation of CD4+Foxp3- T Cells into Peripherally Derived Regulatory T Cells.J Immunol. 2019 Jul 15;203(2):370-378. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900388. Epub 2019 Jun 5. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31167776 Free PMC article.
-
Blockage of TIM-3 relieves lupus nephritis by expanding Treg cells and promoting their suppressive capacity in MRL/lpr mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Sep;110:108971. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108971. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35777268
-
Age-Dependent Bi-Phasic Dynamics of Ly49+CD8+ Regulatory T Cell Population.Aging Cell. 2025 Apr;24(4):e14461. doi: 10.1111/acel.14461. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 39696807 Free PMC article.
-
CD8+ Regulatory T Cell - A Mystery to Be Revealed.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 18;12:708874. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.708874. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484208 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization and effective expansion of CD4-CD8- TCRαβ+ T cells from individuals living with type 1 diabetes.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Dec 17;33(1):101400. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101400. eCollection 2025 Mar 13. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 39877593 Free PMC article.
-
T Cell Resistance: On the Mechanisms of T Cell Non-activation.Immune Netw. 2024 Dec 19;24(6):e42. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e42. eCollection 2024 Dec. Immune Netw. 2024. PMID: 39801736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helios as a Potential Biomarker in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and New Therapies Based on Immunosuppressive Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 29;25(1):452. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010452. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

