Novel roles of METTL1/WDR4 in tumor via m7G methylation
- PMID: 35784404
- PMCID: PMC9217986
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.05.009
Novel roles of METTL1/WDR4 in tumor via m7G methylation
Abstract
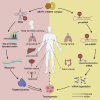
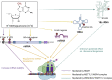
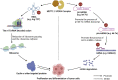
As one of the prevalent posttranscriptional modifications of RNA, N7-methylguanosine (m7G) plays essential roles in RNA processing, metabolism, and function, mainly regulated by the methyltransferase-like 1 (METTL1) and WD repeat domain 4 (WDR4) complex. Emerging evidence suggests that the METTL1/WDR4 complex promoted or inhibited the processes of many tumors, including head and neck, lung, liver, colon, bladder cancer, and teratoma, dependent on close m7G methylation modification of tRNA or microRNA (miRNA). Therefore, METTL1 and m7G modification can be used as biomarkers or potential intervention targets, providing new possibilities for early diagnosis and treatment of tumors. This review will mainly focus on the mechanisms of METTL1/WDR4 via m7G in tumorigenesis and the corresponding detection methods.
Keywords: METTL1; N7-methylguanosine; WDR4; tRNA; tumor.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest related to this study. This manuscript has been read and approved by all the authors and has not been submitted to or is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

