Genetic polymorphisms and phylogenetic analyses of the Ü-Tsang Tibetan from Lhasa based on 30 slowly and moderately mutated Y-STR loci
- PMID: 35784414
- PMCID: PMC9245999
- DOI: 10.1080/20961790.2020.1810882
Genetic polymorphisms and phylogenetic analyses of the Ü-Tsang Tibetan from Lhasa based on 30 slowly and moderately mutated Y-STR loci
Abstract
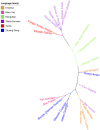
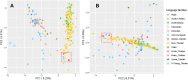
As a result of the expansion of old Tibet on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Tibetans diverged into three main branches, Ü-Tsang, Amdo, and Kham Tibetan. Ü-Tsang Tibetans are geographically distributed across the wide central and western portions of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau while Lhasa is the central gathering place for Tibetan culture. The AGCU Y30, a 6-dye fluorescence kit including 30 slowly and moderately mutated Y-STR loci, has been validated for its stability and sensitivity in different biomaterials and diverse Chinese populations (Han and other minorities), and widely used in the practical work of forensic science. However, the 30 Y-STR profiling of Tibetan, especially for Ü-Tsang Tibetan, were insufficient. We utilized the AGCU Y30 to genotype 577 Ü-Tsang Tibetan unrelated males from Lhasa in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to fill up the full and accurate Y-STR profiles. A total of 552 haplotypes were observed, 536 (97.10%) of which were unique. One hundred and ninety-four alleles were observed at 26 single copy loci and the allelic frequencies ranged from 0.0017 to 0.8180. For the two multi-copy loci DYS385a/b and DYS527a/b, 64 and 36 allelic combinations were observed, respectively. The gene diversity (GD) values ranged from 0.3079 at DYS391 to 0.9142 at DYS385a/b and the overall haplotype diversity (HD) was 0.9998, and its discrimination capacity (DC) was 0.9567. The population genetic analyses demonstrated that Lhasa Ü-Tsang Tibetan had close relationships with other Tibetan populations from Tibet and Qinghai, especially with Ü-Tsang Tibetan. From the perspective of Y haplogroups, the admixture of the southward Qiang people with dominant haplogroup O-M122 and the northward migrations of the initial settlers of East Asia with haplogroup D-M175 hinted the Sino-Tibetan homologous, thus, we could not ignore the gene flows with other Sino-Tibetan populations, especially for Han Chinese, to characterize the forensic genetic landscape of Tibetan.
Keywords: AGCU Y30; Forensic sciences; O-M122; Y-STR; forensic genetics; phylogenetic analysis; Ü-Tsang Tibetan.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Taylor & Francis Group on behalf of the Academy of Forensic Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ben DZA. [Tibetan ethical thought in the prosperous period of the Tubo Dynasty]. Qinghai Social Sci. 1985;4:80–87. Chinese.
-
- Madsen DR, Ma H, Brantingham PJ, et al. . The Late Upper Paleolithic occupation of the northern Tibetan Plateau margin. J Archaeolog Sci. 2006;33:1433–1444.
-
- Aldenderfer M. Peopling the Tibetan plateau: insights from archaeology. High Alt Med Biol. 2011;12:141–147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

