Small mobile conditional cash transfers (mCCTs) of different amounts, schedules and design to improve routine childhood immunization coverage and timeliness of children aged 0-23 months in Pakistan: An open label multi-arm randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 35784436
- PMCID: PMC9241101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101500
Small mobile conditional cash transfers (mCCTs) of different amounts, schedules and design to improve routine childhood immunization coverage and timeliness of children aged 0-23 months in Pakistan: An open label multi-arm randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Cost-effective demand-side interventions are needed to increase childhood immunization. Multiple studies find tying income support programs (≥USD 50 per year) to immunization raises coverage. Research on maximizing impact from small mobile-based conditional cash transfers (mCCTs) (≤USD 15 per fully immunized child) delivered in lower-income settings remains sparse.
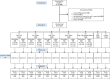
Methods: Participants in Karachi, Pakistan, were individually randomized into a seven arm, factorial open label study with five mCCT arms, one reminder (SMS) only arm, and one control arm. The mCCT arms varied by amount (high ∼USD 15 per fully immunized child versus low ∼USD 5 per fully immunized child), schedule (flat versus rising payments over the schedule), design (certain versus lottery payments), and payment method (airtime or mobile money). Children were enrolled at BCG, pentavalent-1 (penta-1) or pentavalent-2 (penta-2) vaccination and followed until at least 18 months of age. A serosurvey in 15% sub-sample validated reported study coverage. The full immunization coverage (FIC) at 12 months (primary outcome) was analyzed using logit regression. ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03355989), 3ie registry (58f6ee7725fc1), and AEA RCT Registry (AEARCTR-0001953).
Findings: Between November 6, 2017, and October 10, 2018, a total of 11,197 caregiver-child pairs were enrolled, with 1598-1600 caregiver-child pairs per arm. FIC at 12 months was statistically significantly higher for any mCCT versus SMS (OR:1.18, 95% CI: 1.05-1.33; p = 0.005). Within the mCCT arms, FIC was statistically significantly higher for high versus low amount (OR: 1.16, 95% CI: 1.04-1.29; p = 0.007), certain versus lottery payment (OR: 1.30, 95% CI: 1.17-1.45; p < 0.001) and airtime versus mobile money (OR: 1.17, 95% CI:1.01-1.36; p = 0.043). There was no statistically significant difference between a flat and increasing schedule (OR: 1.03, 95% CI: 0.93-1.15; p = 0.550). SMS had a marginally statistically significant impact on FIC versus control (OR: 1.16, 95% CI: 1.00-1.35; p = 0.046). Findings were similar for up-to-date coverage of penta-3, measles-1 and measles-2 at 18 months.
Interpretation: Small mCCTs (USD 0.8-2.4 per immunization visit) can increase FIC at 12 months and up-to-date coverage at 18 months at USD 23 per additional fully immunized child, in resource-constrained settings like Pakistan. Design details (certainty, schedule and delivery method of mCCTs) matter as much as the size of payments.
Funding: Global Innovation Fund, GiveWell.
Keywords: Conditional cash transfers; Coverage; Immunizations; Incentives; Mobile-based conditional cash transfers; Vaccines.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Immunization Coverage. 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/immunization-coverage. Accessed 8 March 2022.
-
- GAVI. Facts and Figures. https://www.gavi.org/programmes-impact/our-impact/facts-and-figures. Accessed 28 October 2021.
-
- Pakistan Demographic and Health Survey 2017-18 . National Institute of Population Studies (NIPS) and ICF; Islamabad, Pakistan, and Rockville, Maryland, USA: 2019. NIPS and ICF.
-
- Ranganathan M, Lagarde M. Promoting healthy behaviours and improving health outcomes in low and middle income countries: a review of the impact of conditional cash transfer programmes. Prev Med. 2012;55(Suppl):S95–S105. - PubMed
-
- Kremer AHaM. Center for Global Development; Washington, DC: 2009. Pricing and Access: Lessons from Randomized Evaluations in Education and Health CGD. Working Paper 158.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

