Liver Microabscesses in a Premature Neonate With Eosinophilic Colitis
- PMID: 35784499
- PMCID: PMC9246066
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000817
Liver Microabscesses in a Premature Neonate With Eosinophilic Colitis
Abstract
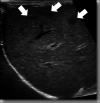
Hepatic abscesses in premature infants are rare with less than 100 case reports documented in literature. We report a case of a premature infant diagnosed with hepatic microabscesses secondary to eosinophilic colitis. A 33 4/7-week preterm female neonate presented with bilious emesis, abdominal distention, and severe hematochezia. Eosinophilic enterocolitis was suspected. Hypoechoic regions in the anterior liver identified on computed tomography were considered liver microabscesses. This unique case exemplifies how prematurity increases the risk of mucosal damage in the presence of eosinophilic colitis causing enteric bacteria to seed into the liver through the portal vein, resulting in hepatic microabscesses.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures
References
-
- Kaijser R. Zur Kenntnis der allergischen affekitonen des verdauungskanals vom standput des chirugen aus. Arch Klin Chir. 1937;188:36–64.
-
- Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113(1):11–28; quiz 29. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources